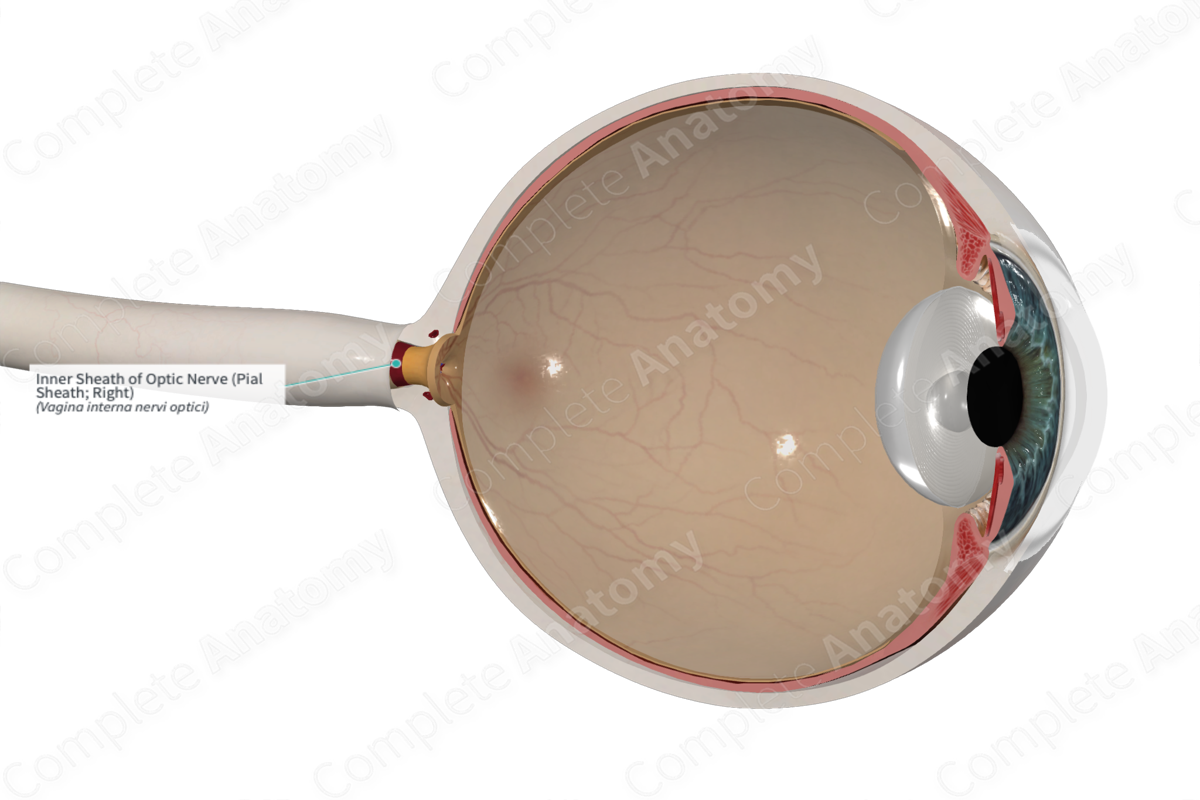
Inner Sheath of Optic Nerve (Pial Sheath; Right)
Vagina interna nervi optici
Read moreQuick Facts
The inner sheath of optic nerve is the internal sheath of the optic nerve, continuous with the pia mater and arachnoid mater (Dorland, 2011).
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
The eye and optic nerve are outgrowths of the brain and as such carry the three layers of meningeal coverings with them. They are called collectively, the optic sheath. Of these, the inner two layers, arachnoid and pia, are referred to collectively as the inner or internal sheath of the optic nerve.
The innermost layer of the inner sheath of the optic nerve is continuous with the pia mater of the brain. It is referred to as the pial sheath of the inner sheath of the optic nerve. As the optic nerve enters the eyeball, the inner sheath becomes continuous with the choroid of the eyeball (Dorland, 2011). The pial sheath is vascular and penetrates the optic nerve, subdividing it into 300–400 fascicles (Hayreh, 1984). This organization gives access to the pial blood vessel to supply the optic nerve (Standring, 2016).
Anatomical Relations
The pial sheath intimately invests the external surface of the optic nerve and sends extensions within its substance. Externally is the cerebrospinal fluid of the subarachnoid space that separates the pial sheath from the arachnoid sheath. These sheaths surround and accompany the optic nerve up to the eyeball where they become continuous with the choroid coat of the eyeball.
Function
Similar to the brain, the pial sheath supports the axons of the optic nerve, providing a route for nutrients and oxygen.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Hayreh, S. S. (1984) 'The sheath of the optic nerve', Ophthalmologica, 189(1-2), pp. 54-63.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.



