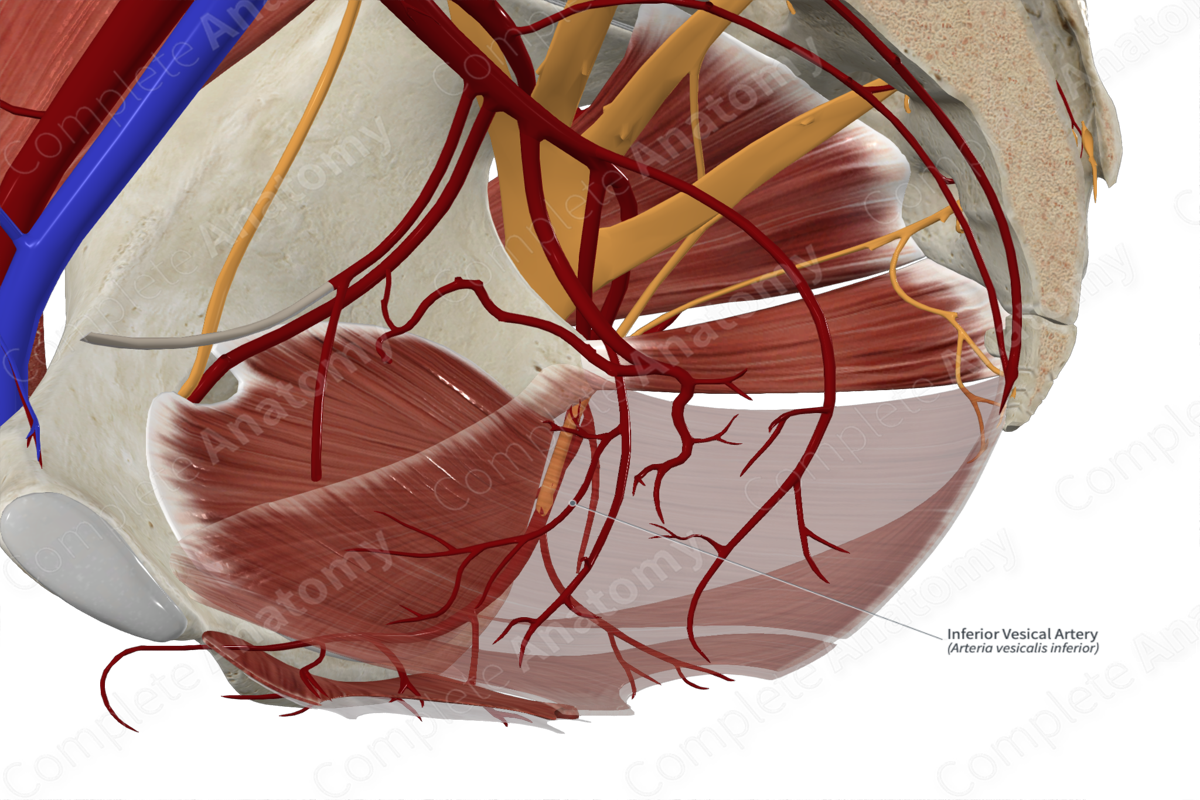
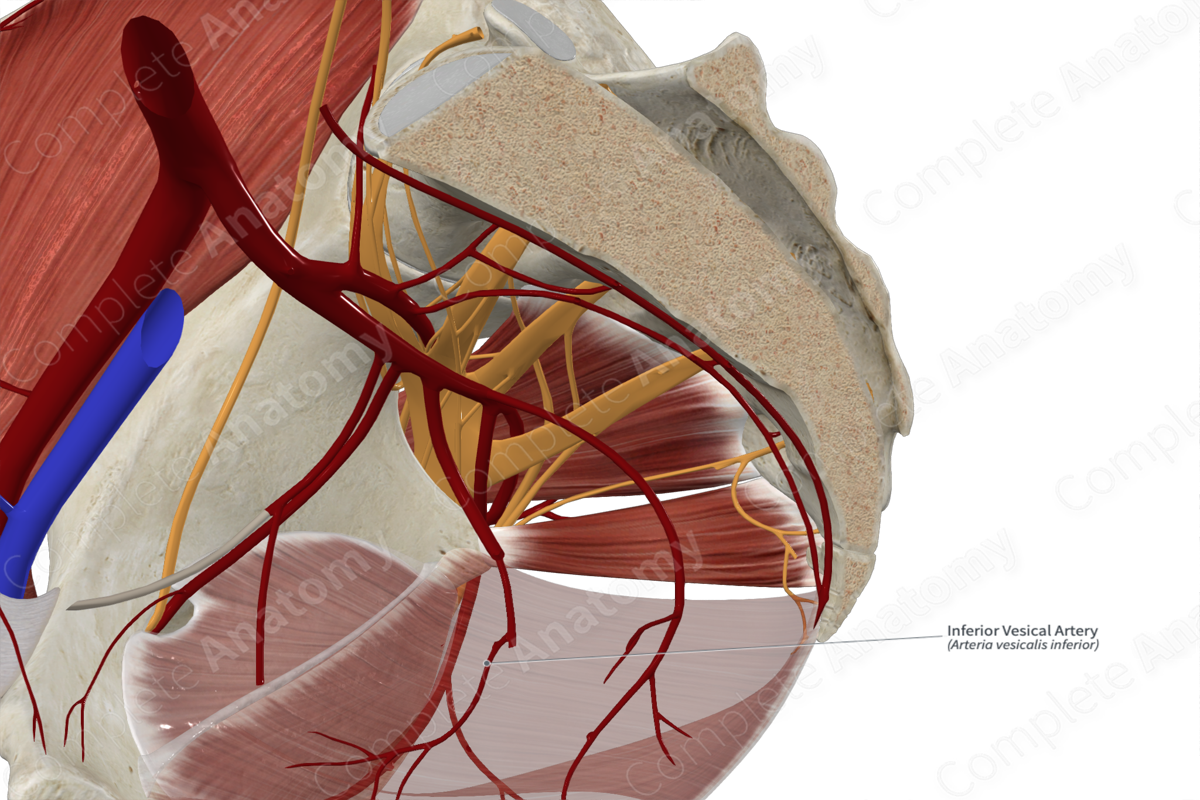
Quick Facts
Origin: Anterior division of internal iliac artery (males) or branch of the vaginal artery (females).
Course: Travels anteriorly to lower portion of bladder and ramifies along its surface.
Branches: Prostatic artery and the artery of the ductus deferens (males).
Supplied Structures: Bladder, prostate, seminal glands, distal ureter, and ductus deferens.
Origin
In males, the inferior vesical artery arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. Sometimes, the vessel may arise directly from the middle rectal artery.
In females, the inferior vesical artery is a branch of the vaginal artery. The vaginal artery is a homologue of the inferior vesical arteries in males as it arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac vein.
Course
The inferior vesical artery travels anteriorly from its origin to enter the lateral ligament of the bladder.
Branches
In males, the inferior vesical artery branches into the prostatic artery and occasionally the artery of the ductus deferens. However, the artery to the ductus deferens is normally a branch of the superior vesical artery.
In females, the artery does not branch, but it does form anastomosis with the superior vesical artery.
Supplied Structures
In males, the artery supplies the bladder, prostate, seminal glands, distal ureter, and ductus deferens.
In females, the artery ramifies on the surface of the bladder in order to supply it.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products