Quick Facts
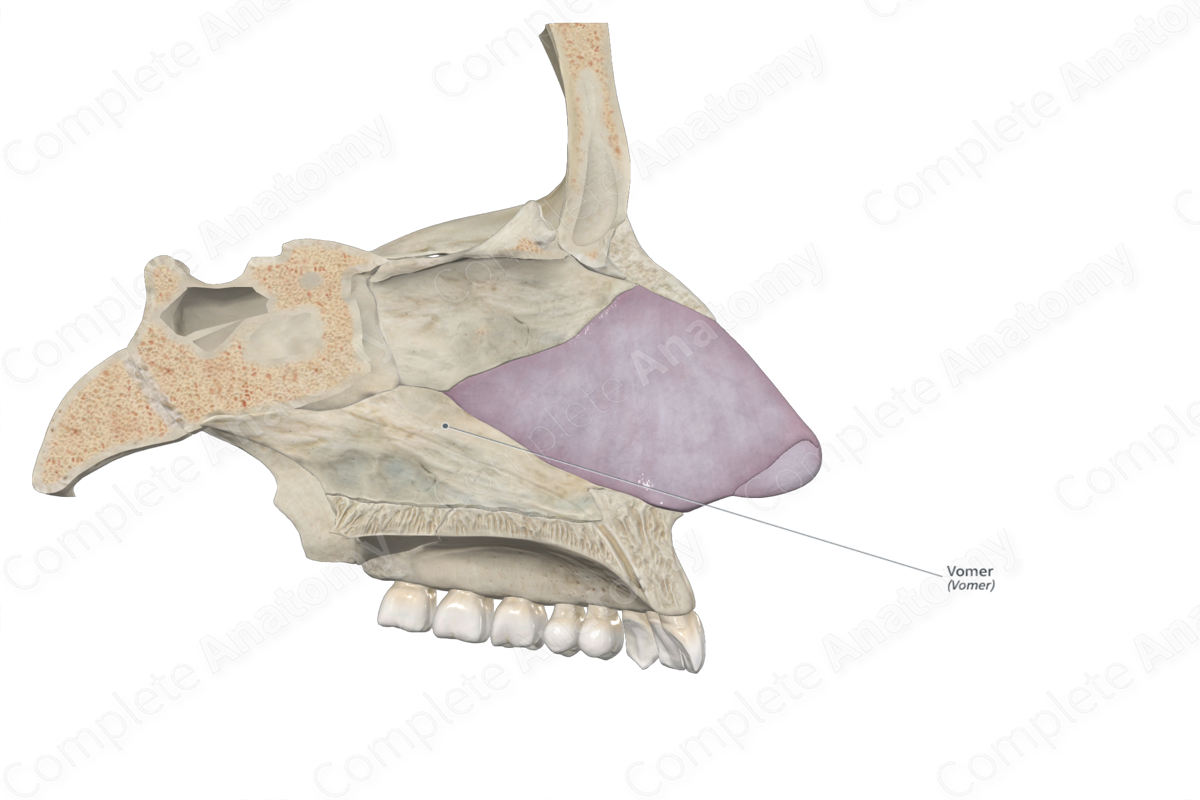
Location: Viscerocranium.
Bone Type: Flat bone.
Key Features: Cuneiform part, alae, lateral surfaces, vomerine groove, vomerine crest of choana, and nasopalatine grooves.
Articulates With: Sphenoid, ethmoid, and palatine bones, and maxillae.
Arterial Supply: Sphenopalatine artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
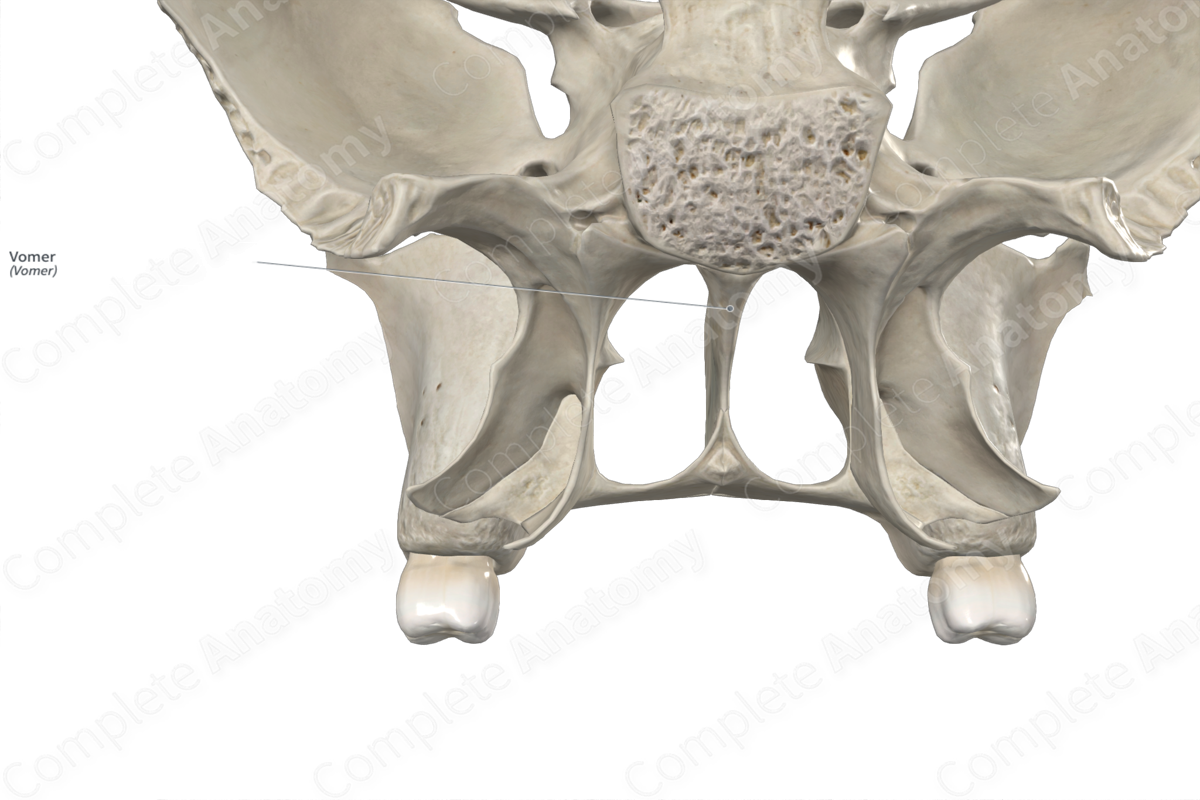
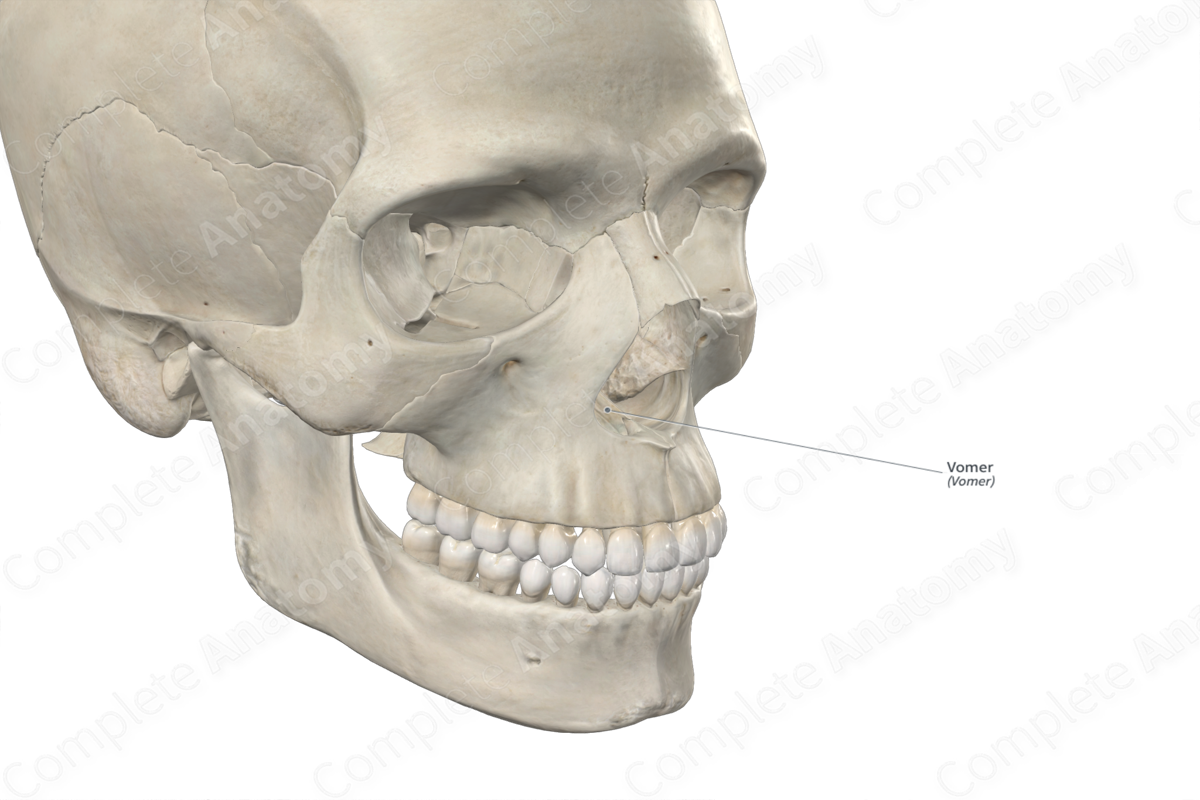
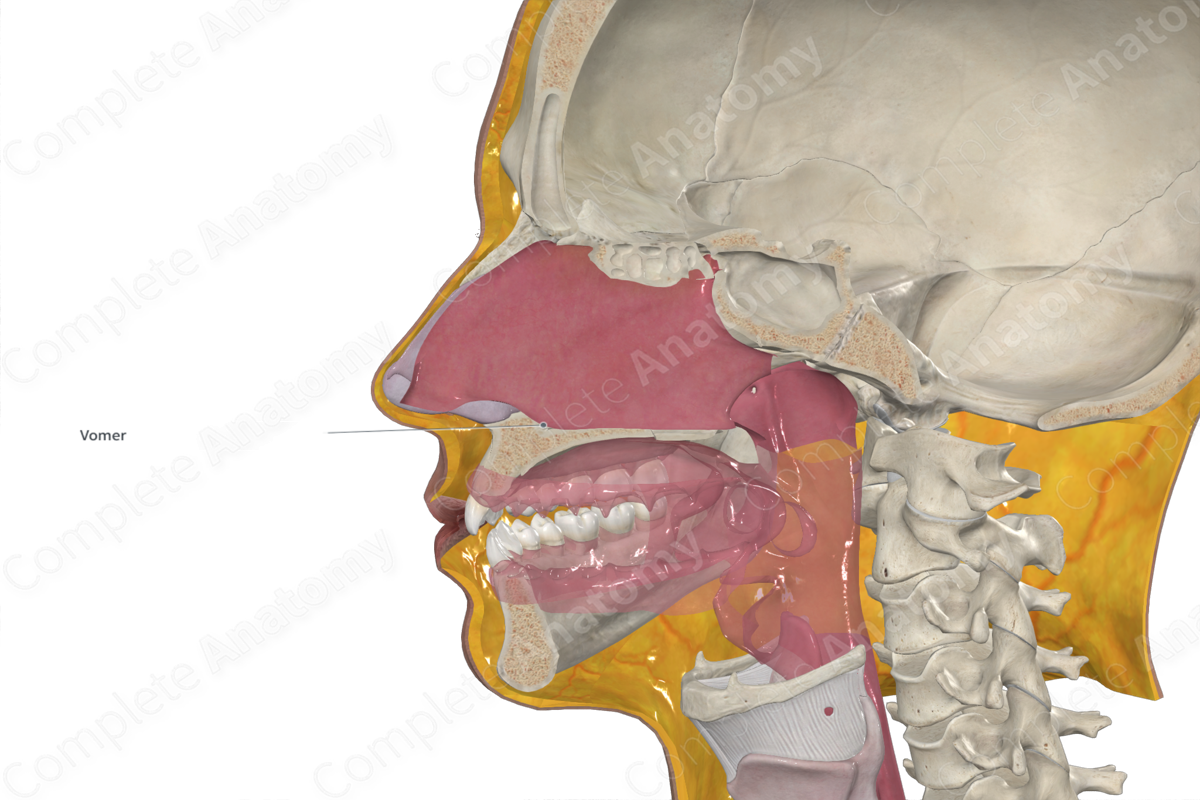
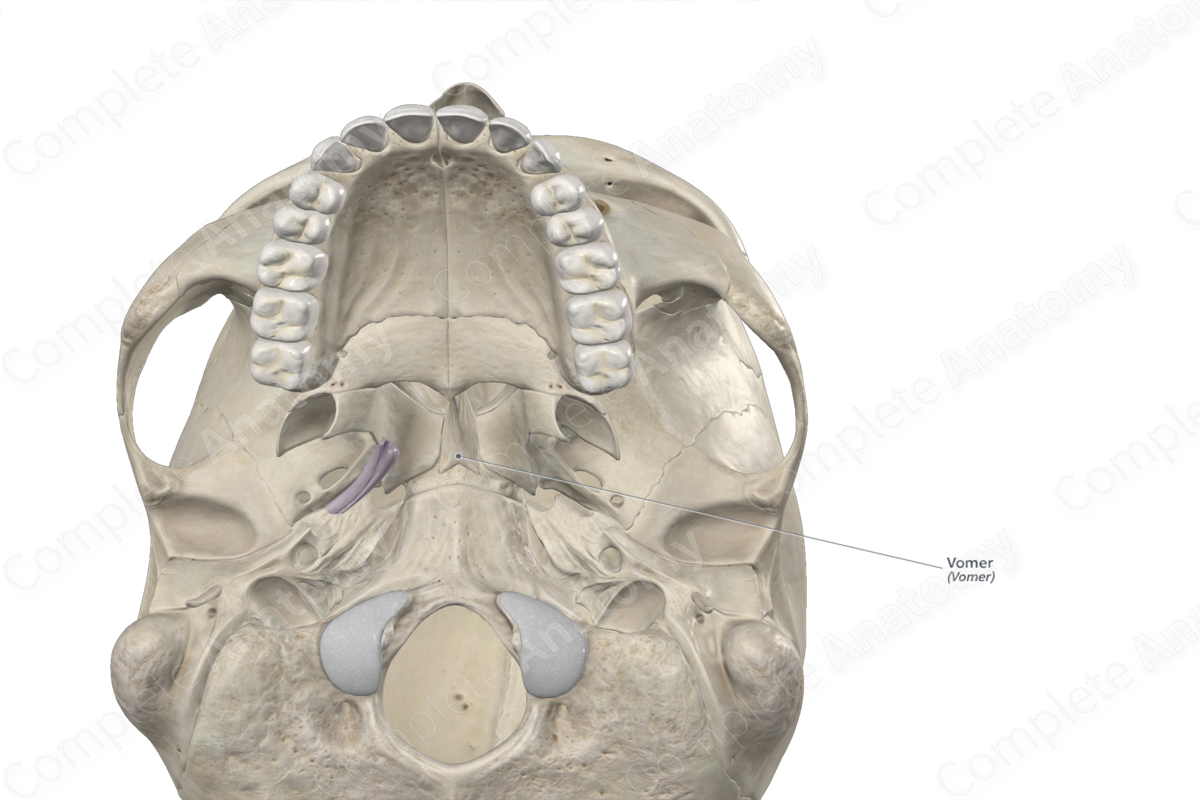
The vomer is a single, thin, quadrilateral bone that is located along the midline between the right and left nasal cavities. It is classified as a flat bone and contributes to the formation of the bony nasal septum, nasal cavities and viscerocranium. The vomer includes the following bony features:
- parts: cuneiform part and alae;
- surfaces: lateral surfaces, and anterior, posterior, superior, and inferior borders;
- landmarks: vomerine groove, vomerine crest of choana, and nasopalatine grooves.
More information regarding these bony features can be found in the Parts, Surfaces and Landmarks tabs for this bone.
The vomer is located:
- inferior to the ethmoid bone;
- medial to the maxillae and inferior nasal conchae.
It articulates with the:
- sphenoid bone at the sphenovomerine suture;
- ethmoid bone;
- maxillae;
- palatine bones.
Ossification
Ossification of the vomer occurs at two ossification centers, with one found in the right half and the other found in the left half, which appear in utero during the second month. They begin to fuse with each other in utero during the third month, with fusion usually being completed by puberty (Standring, 2016).
Variations
In some individuals:
- the shape of the vomer can vary;
- the vomer may be absent (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Fracture of vomer
- Nasal septum deviation
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. and Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products