Quick Facts
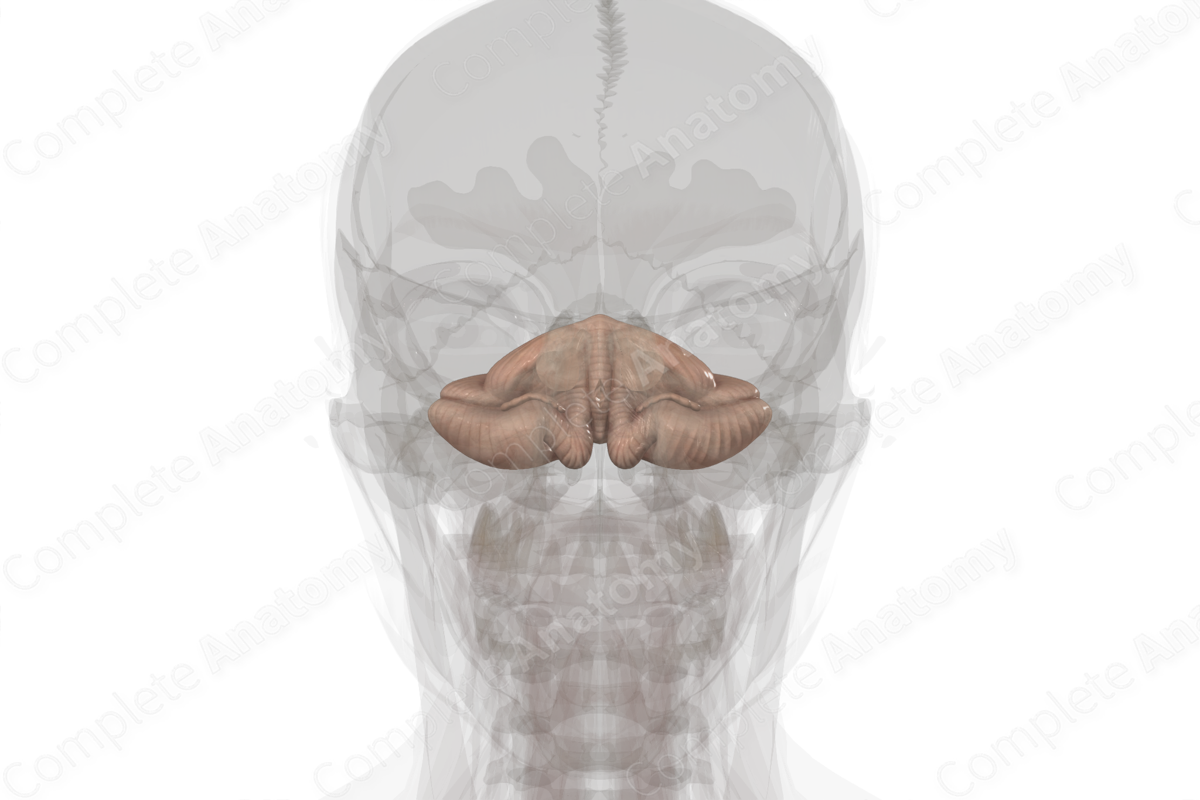
The cerebellum belongs to the metencephalon division of the rhombencephalon, or hindbrain. It is located beneath the cerebral hemispheres and is identified by the series of shallow grooves that run in parallel across it.
It is connected to the brainstem by thick bundles of nervous fibers called peduncles, which transmit signals to and from the cerebellum, cerebrum, midbrain and spinal cord. The cerebellum lies dorsal to the pons, which acts as a bridge of white matter, transmitting signals between the cerebrum and the cerebellum.
The cerebellum is heavily involved in the control and learning of movement, sending continuous adjustment signals to the motor output of the brain to refine movements and to adjust posture. While it is heavily implicated in motor control and refinement, the cerebellum is also involved in other higher order functions such as language, attention and emotional learning.
The interior of the cerebellum consists of a series of white matter tracts, which radiate from a central stem of white matter towards the grey matter exterior of the cerebellum. The tree-like appearance of these tracts gives rise to their name - the arbor vitae.
The cerebellum consists of three anatomically distinct but continuous regions - the two cerebral hemispheres on either side, and the vermis that connects them in the middle. A cerebellar tonsil protrudes from the undersurface of the cerebellum and is continuous with the vermis. Each cerebellar hemisphere is further divided into three lobes, a posterior lobe, an anterior lobe and a flocculonodular lobe.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Cerebellum: Video, Causes, & Meaning

Cerebellum: Symptoms, Causes, Videos & Quizzes | Learn Fast for Better Retention!





