Quick Facts
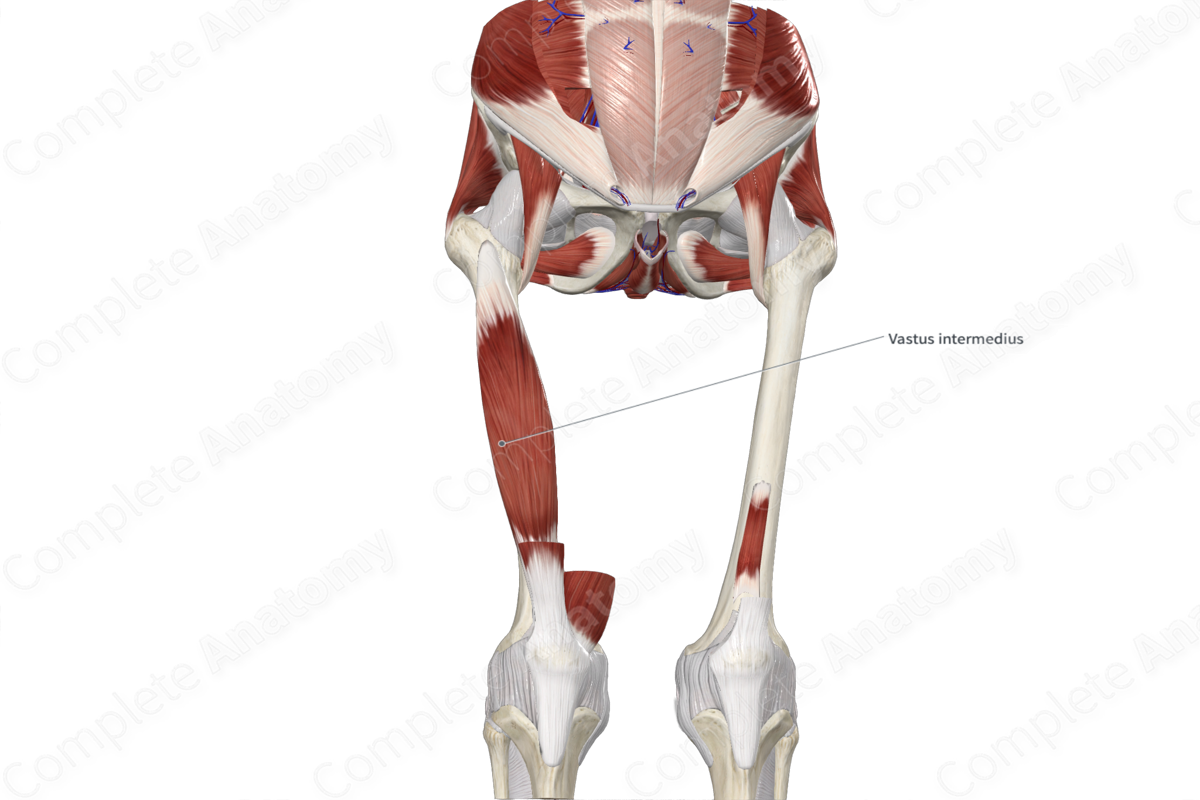
Origin: Anterior and lateral surfaces of body of femur.
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity, via tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle and patellar ligament.
Action: Extends leg at knee joint.
Innervation: Femoral nerve (L2-L4).
Arterial Supply: Deep femoral artery.
Origin
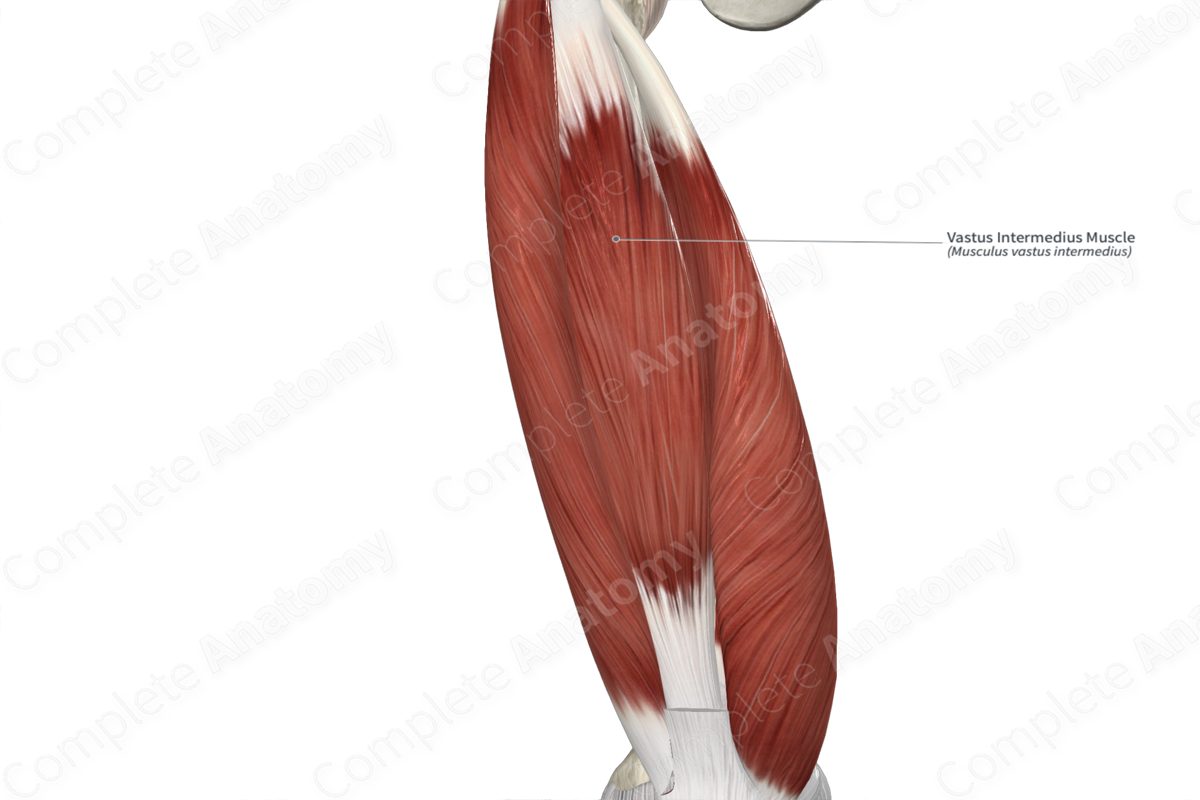
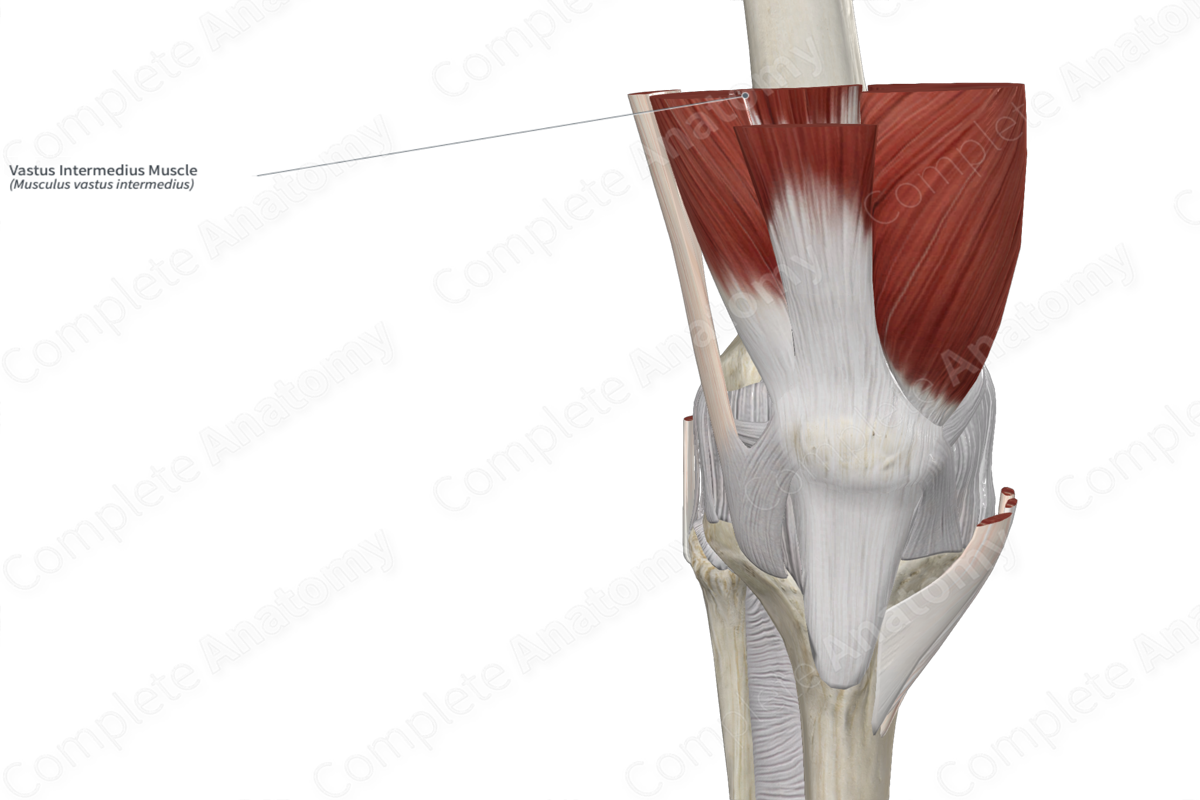
The vastus intermedius muscle originates from the anterior and lateral surfaces of the proximal two thirds of the body of the femur.
Insertion
The fibers of the vastus intermedius muscle travel inferiorly and converge with the fibers of the rectus femoris, vastus medialis and vastus lateralis muscles to form the tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle. The fibers of this tendon travel superficial to the patella, where they become continuous with the patellar ligament, which inserts onto the tibial tuberosity.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
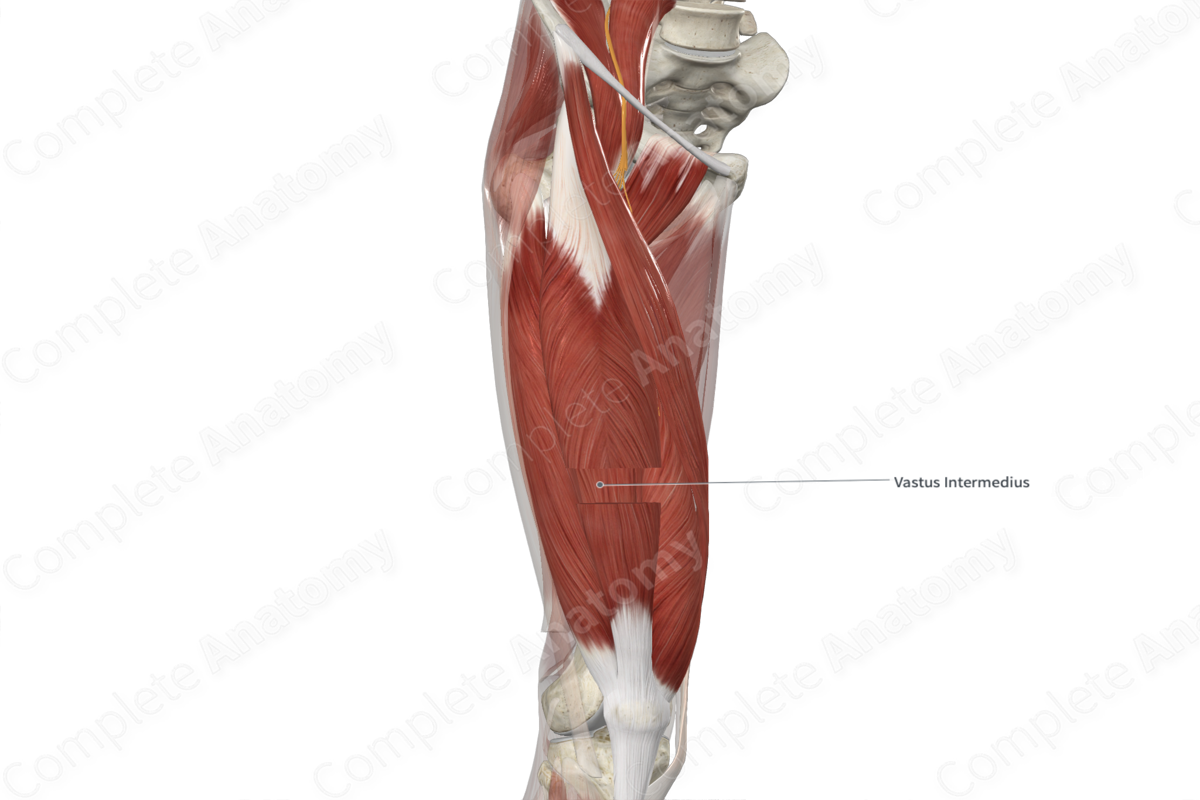
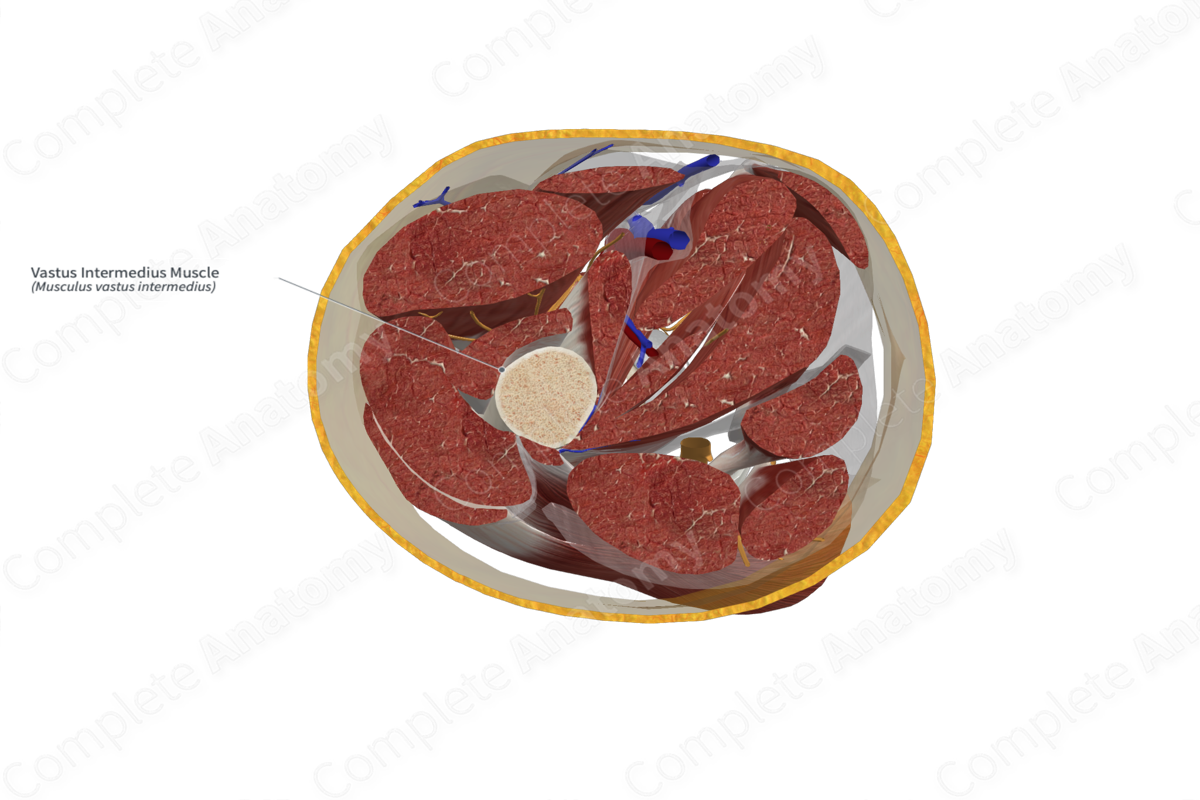
The vastus intermedius muscle is one of the four muscles that form the quadriceps femoris muscle, the other three being the rectus femoris, vastus medialis and vastus lateralis muscles. It is a long, thick, bipennate type of skeletal muscle.
It is located:
- anterior (superficial) to the femur and the articularis genus muscle;
- posterior (deep) to the rectus femoris muscle;
- medial to the vastus lateralis muscle;
- lateral to the vastus medialis muscle.
Actions & Testing
The vastus intermedius muscle extends the leg at the knee joint, via the tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle and patellar ligament. It cannot be tested in isolation, therefore all four muscles of the quadriceps femoris are tested simultaneously by extending the leg at the knee joint against resistance while lying in the supine position with the hip flexed (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Patellar instability
- Patellar pain
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products