Quick Facts
The epithelial portion of the hair follicle is divided into the inner root sheath and the outer root sheath. The inner root sheath has three layers: Huxley layer, Henle layer, and the cuticle of the root sheath. The outer root sheath does not have distinct layers and merges with the epidermis near the skin surface (Dorland, 2011).
Structure/Morphology
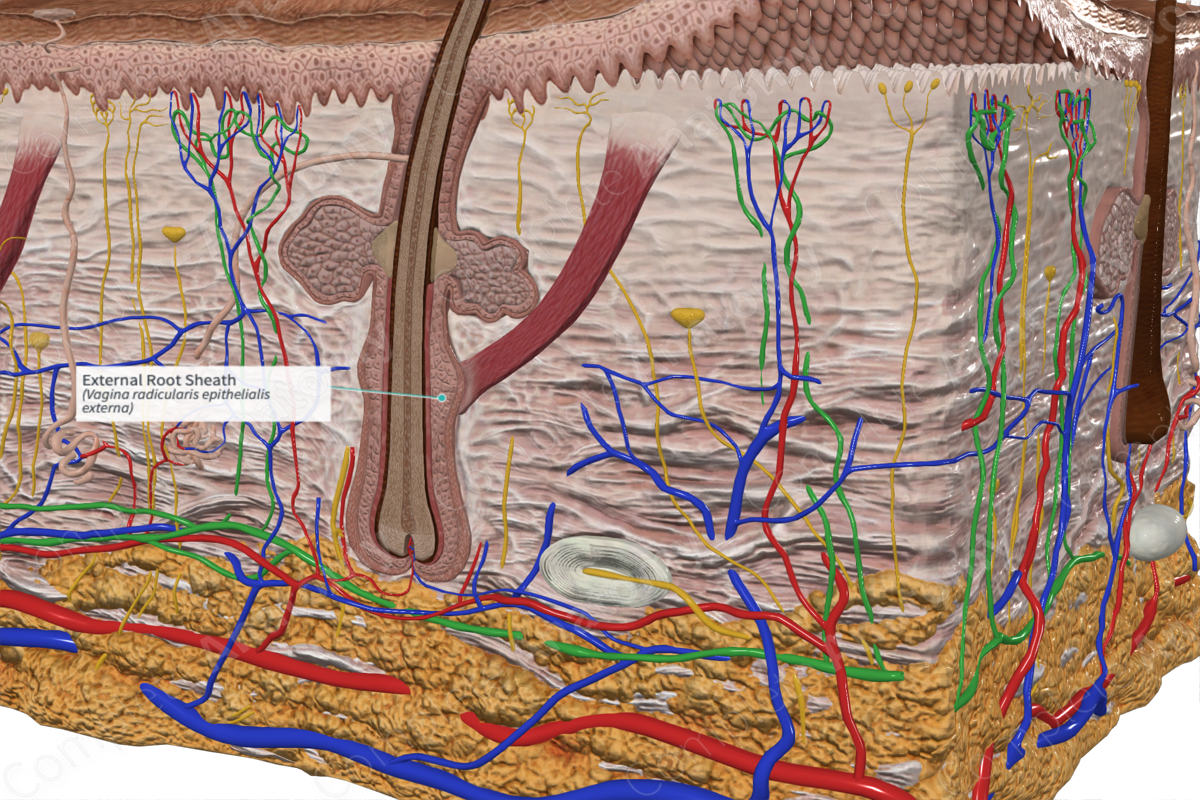
The external root sheath envelops the inner root sheath and the hair shaft. It extends from the hair bulb to the epidermis and opens up to the surface of the skin. This layer and the internal root sheath are produced by the rapidly reproducing matrix cells found in the periphery of the follicular bulb. It shares a cellular composition found in the epidermis along the majority of its length. However, at the level of the hair bulb, the cells are more consistent with that of the stratum basale of the epidermis (Standring, 2016; Joshi, 2011).
Within the external root sheath lies the bulge, this is an enlarged area of the external root sheath just below the level of the sebaceous gland which is a reservoir of stem cells of the hair follicle. The bulge is also the site at which the arrector pili muscle will attach to the hair follicle. The External Root Sheath is separated by the external layer of the hair follicle, the Connective Tissue Sheath, by the Glassy Membrane (a form of basement membrane) (Ohyama, 2007; Young, 2006).
Function
Although the external root sheath does not partake in the formation of the hair shaft, it contains functional units of the hair follicle including the bulge of the hair follicle which is a region containing stem cells. It also gives rise to the sebaceous gland of the hair follicle which produces sebum which lubricates and protects the hair shaft and skin surface (Niderla-Bielińska, Jankowska-Steifer and Moskalewski, 2008; Niemann, 2009).
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Joshi, R. S. (2011) 'The Inner Root Sheath and the Men Associated with it Eponymically', Int J Trichology, 3(1), pp. 57-62.
Niderla-Bielińska, J., Jankowska-Steifer, E. and Moskalewski, S. (2008) Structure and function of outer and inner root sheath of hair follicle. Stem cells of hair follicle.
Niemann, C. (2009) 'Differentiation of the sebaceous gland', Dermato-Endocrinology, 1(2), pp. 64-67.
Ohyama, M. (2007) 'Hair follicle bulge: a fascinating reservoir of epithelial stem cells', J Dermatol Sci, 46(2), pp. 81-9.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series: Elsevier Limited.
Young, B. (2006) Wheater's Functional Histology: A Text and Colour Atlas. Student consult: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier.
