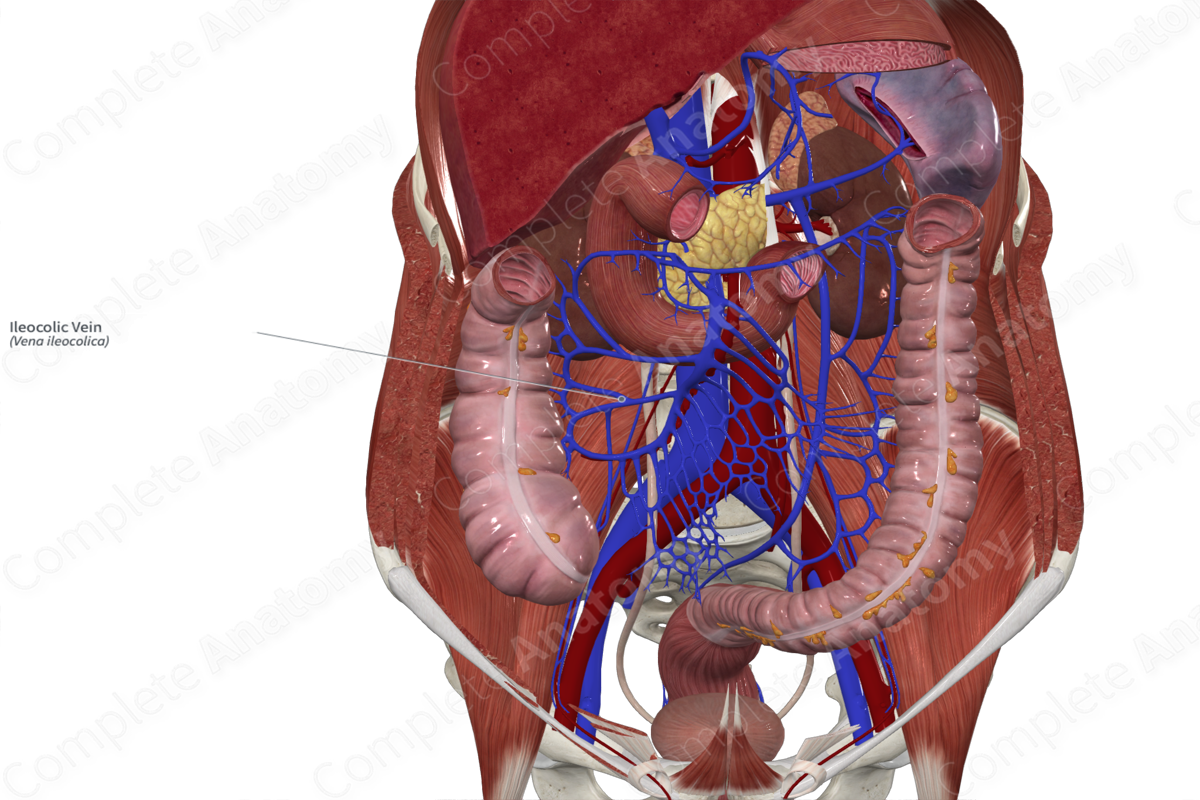
Quick Facts
Origin: Junction of the ileum and cecum.
Course: Travels obliquely from the ileocecal junction to drain into the superior mesenteric vein.
Tributaries: Appendicular and cecal veins.
Drainage: Distal ileum, cecum, appendix, and proximal ascending colon.
Origin
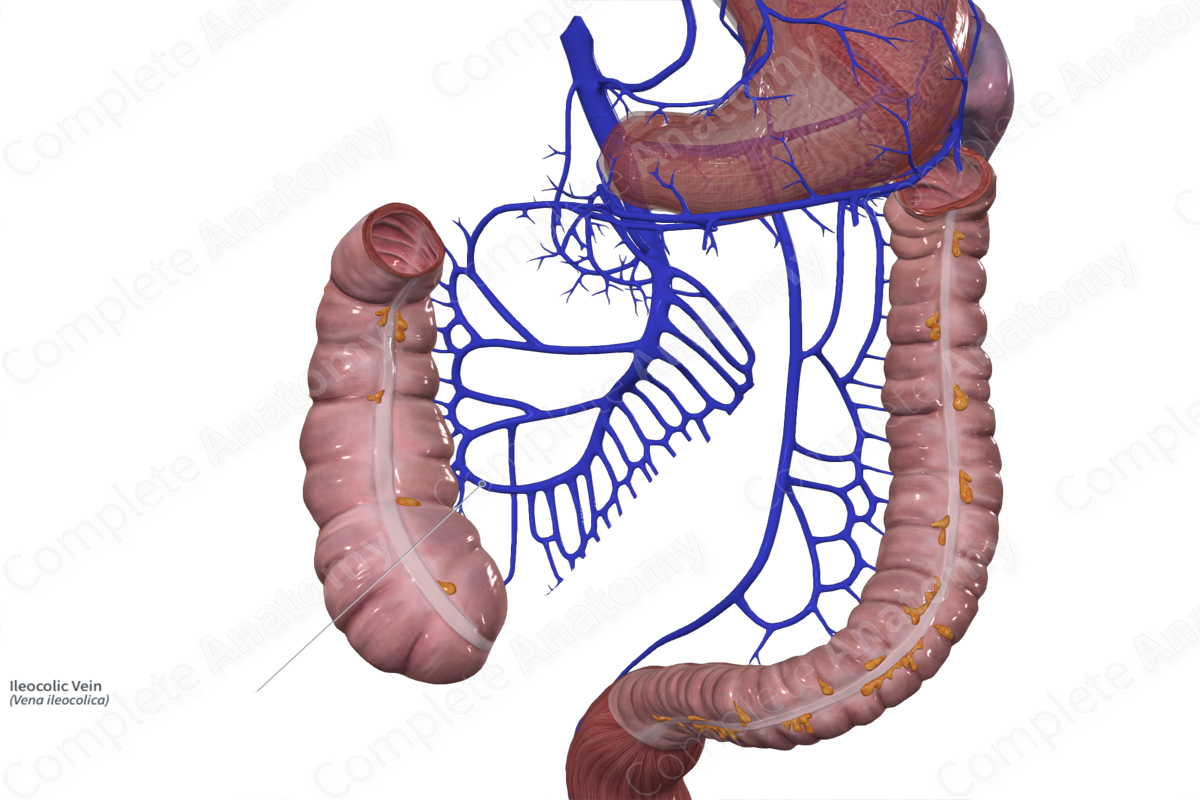
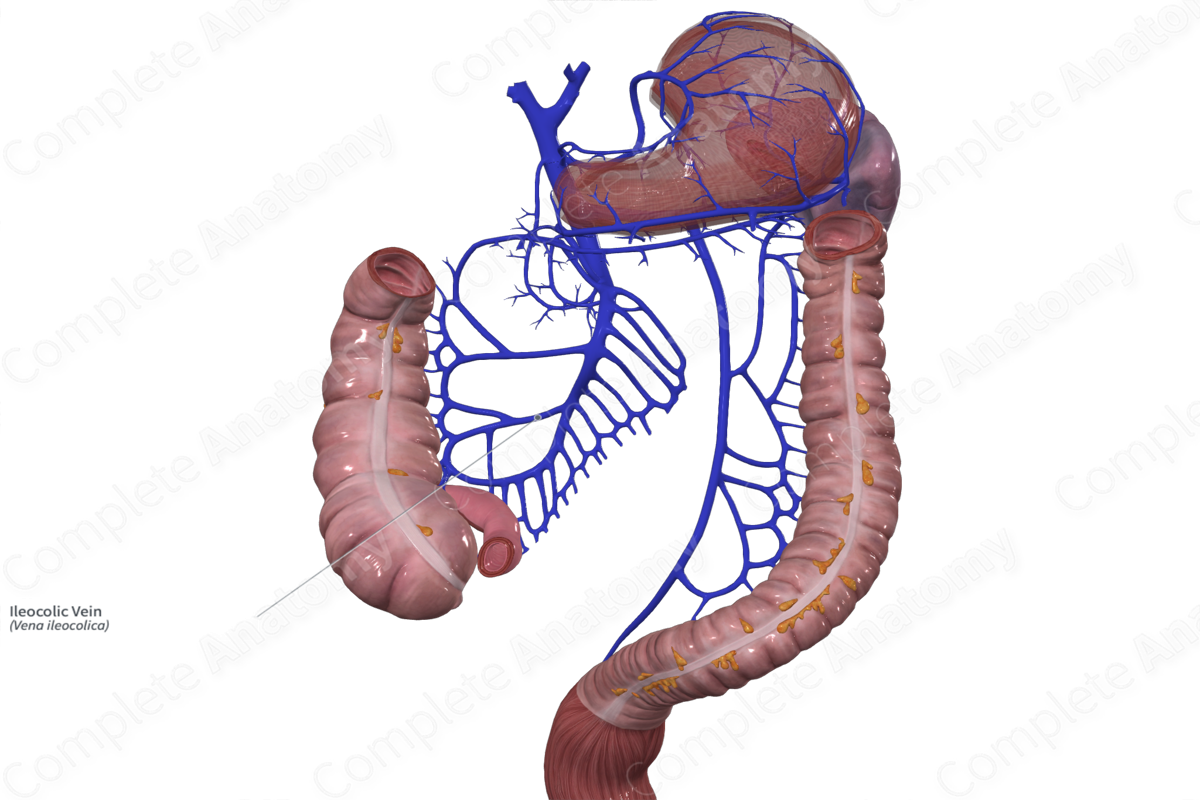
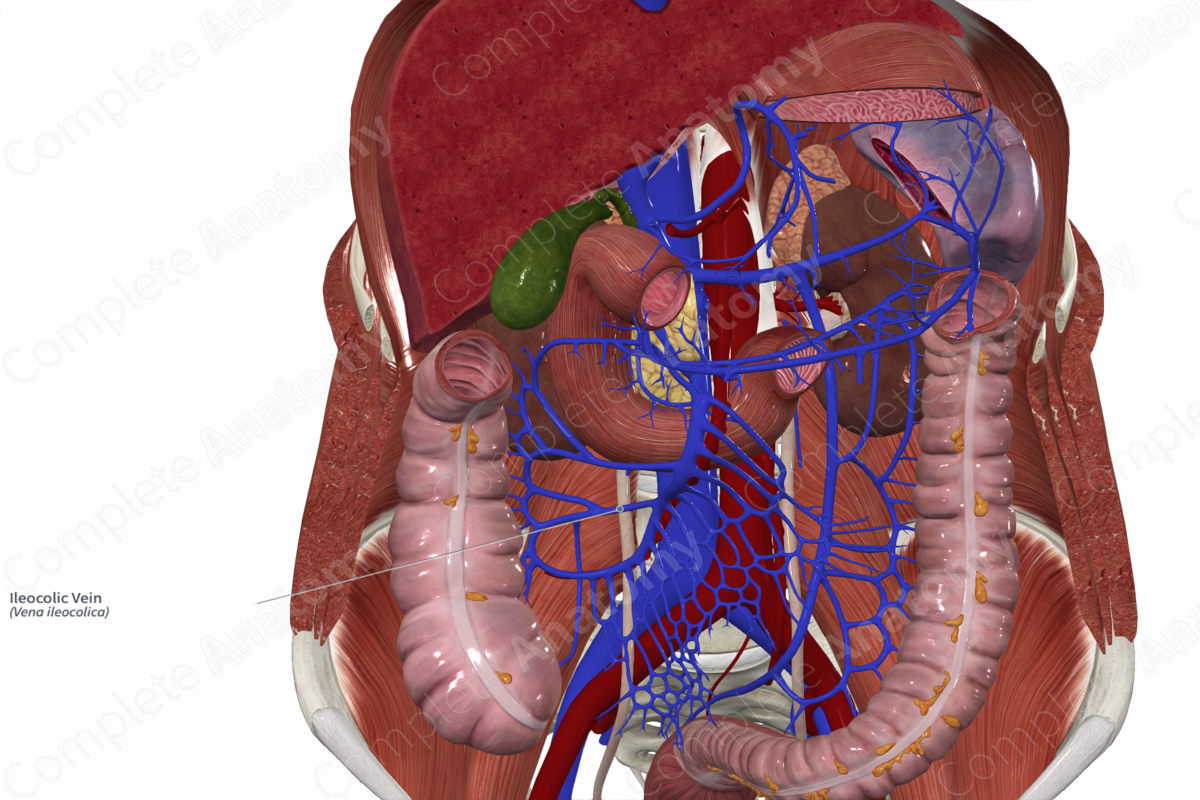
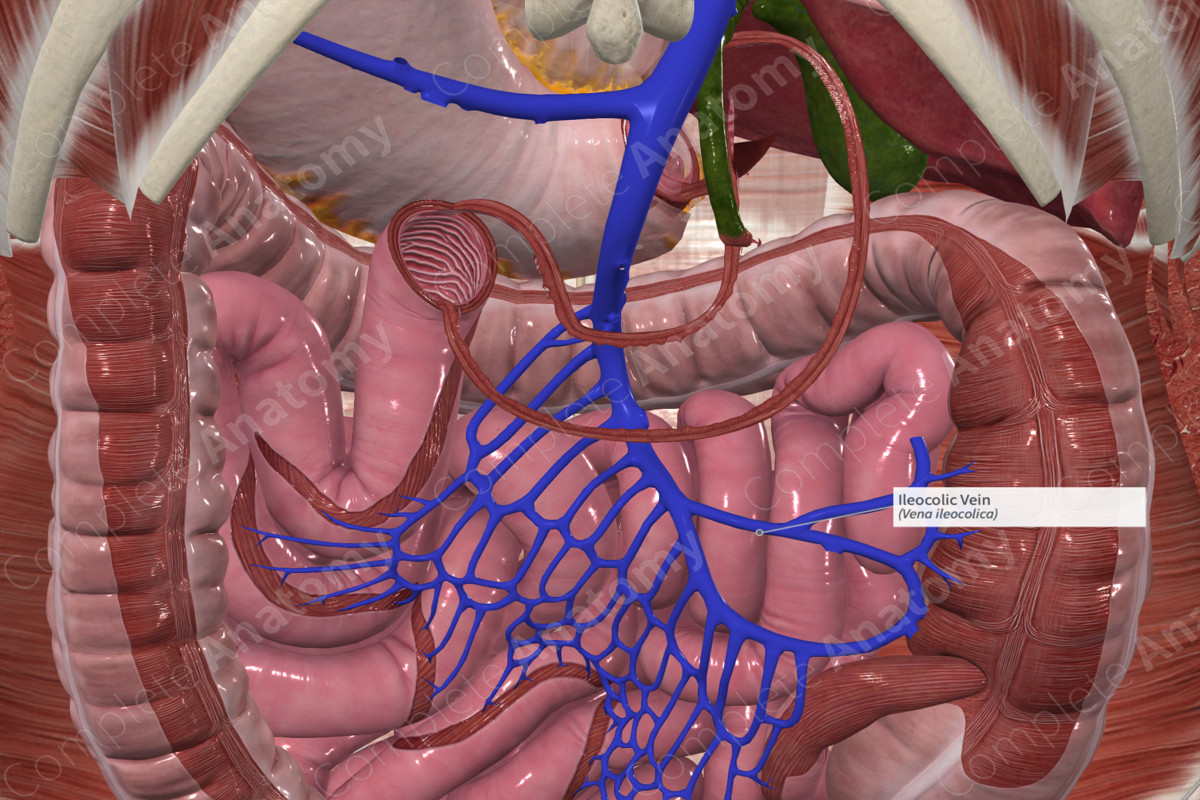
The ileocolic vein originates adjacent to the ileocolic artery near the surface of the ileum.
Course
The appendicular and cecal veins merge to form the ileocolic vein. The ileocolic vein travels obliquely from the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, superiorly and medially towards to the midline of the body. The ileocolic vein drains directly into the superior mesenteric vein.
Tributaries
The ileocolic vein receives the appendicular and cecal veins.
Structures Drained
The ileocolic vein drains the distal ileum, appendix, cecum, and proximal ascending colon.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Appendectomy
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products