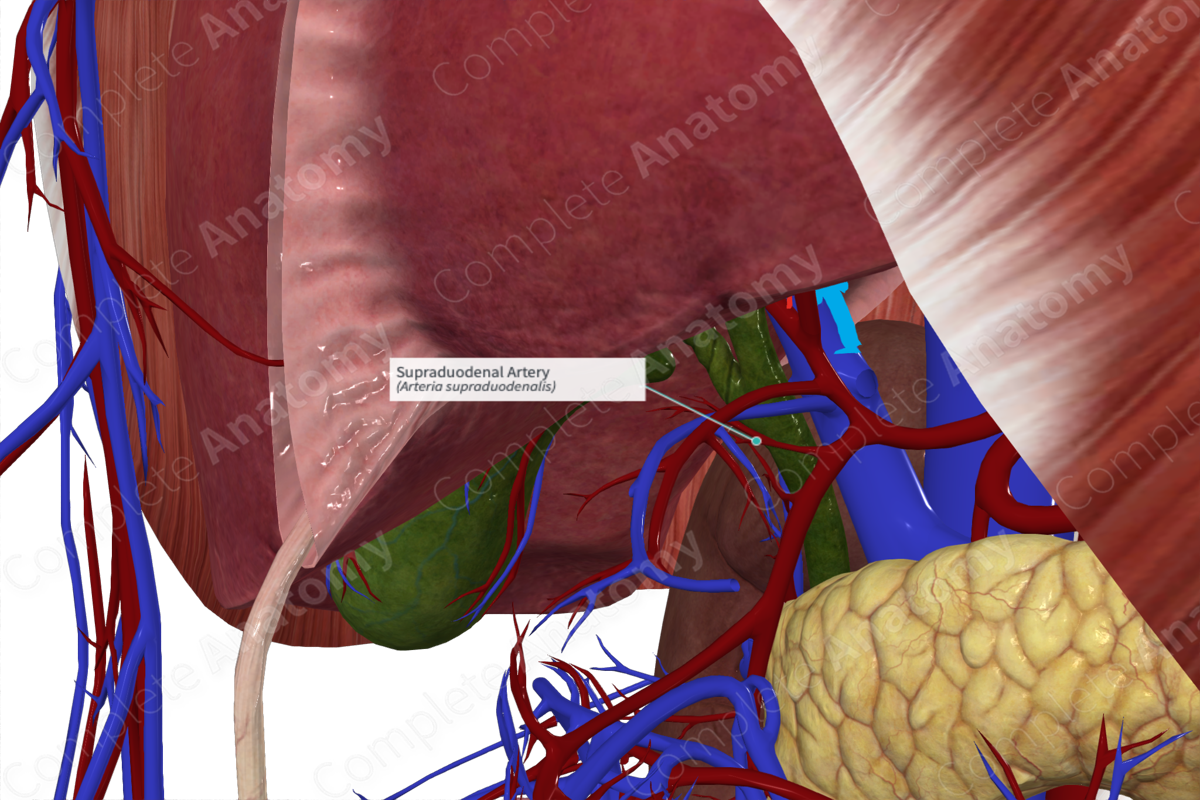
Quick Facts
Origin: Gastroduodenal artery.
Course: Passes superiorly over the superior surface of the first part of the duodenum.
Branches: Unnamed anastomotic branches.
Supplied Structures: Superior, right, and anterior surfaces of the first part of the duodenum, extending into the second part.
Origin
The supraduodenal artery arises most frequently from the proximal portion of the gastroduodenal artery, but is highly variable [26.6% of cadavers examined in one study (Bianchi and Albanèse, 1989)]. Other common sites of origin include the common, left, and right hepatic arteries.
Course
The supraduodenal artery emerges close to the origin of the gastroduodenal artery, posterior to the first part of the duodenum. It passes superiorly, arching over the superior surface of the first part and the left side of second part of the duodenum.
Branches
The supraduodenal artery gives rise to many unnamed anastomotic branches with those from the right gastric artery and the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery.
Supplied Structures
The supraduodenal artery supplies the superior, right, and anterior surfaces of the first part of the duodenum, extending into second part. It also variably contributes to vascularization of the distal portion of the common bile duct (Bianchi and Albanèse, 1989).
References
Bianchi, H. F. and Albanèse, E. F. (1989) 'The supraduodenal artery', Surg Radiol Anat, 11(1), pp. 37-40.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




