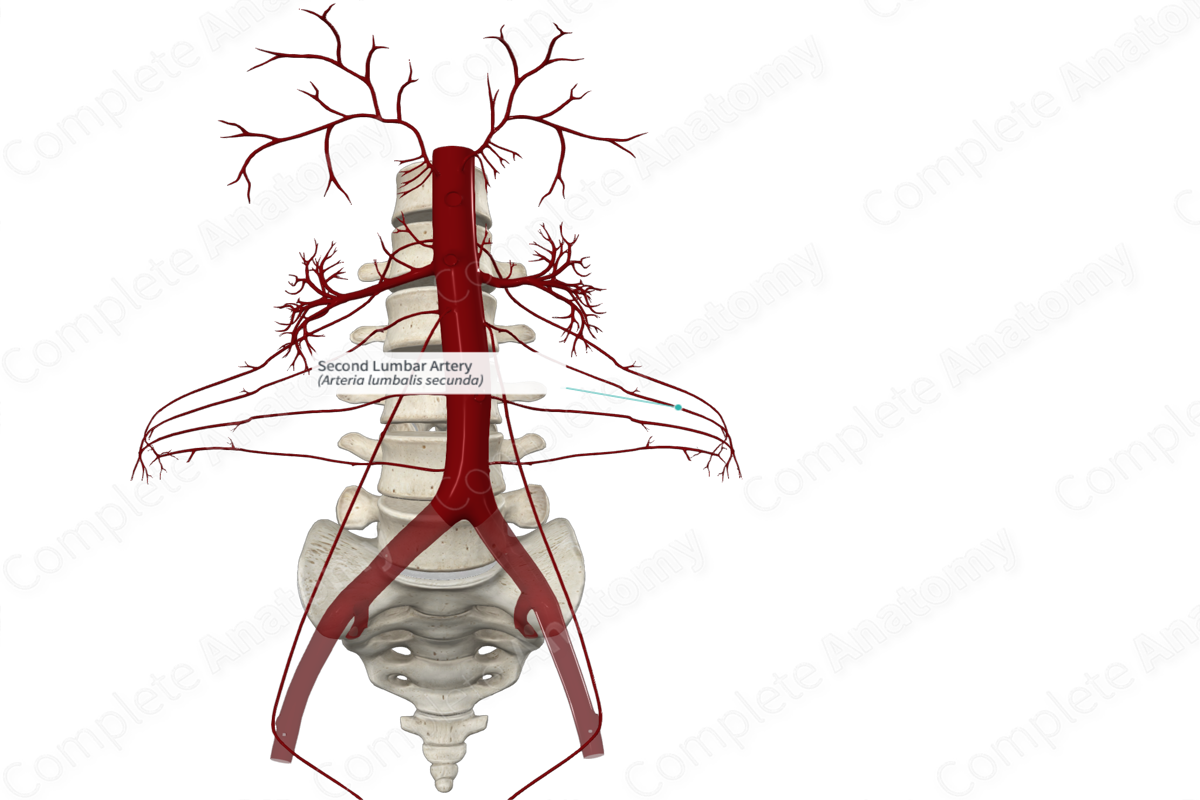
Quick Facts
Origin: Abdominal aorta.
Course: Travel laterally and then in an anteromedial direction.
Branches: Dorsal branch.
Supplied Structures: Abdominal wall.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The lumbar arteries arise as paired branches from the posterolateral aspect of the abdominal aorta.
Course
The lumbar arteries course in a posterolateral direction behind the sympathetic chain and posterior to the crura of the diaphragm, the psoas major, and the quadratus lumborum muscles. On the right-hand side, they also pass behind the inferior vena cava.
The lumbar arteries curve in an anterolateral direction and traverse the posterior edge of the transversus abdominis muscle. They continue between the internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis muscle and terminates near the rectus abdominis muscle.
Branches
A dorsal branch originates from each lumbar artery near its origin and travels posteriorly within the musculature of the back.
Supplied Structures
The lumbar arteries contribute to the muscular, fascial, and cutaneous supply of the anterior, lateral, and posterior abdominal wall.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




