Quick Facts
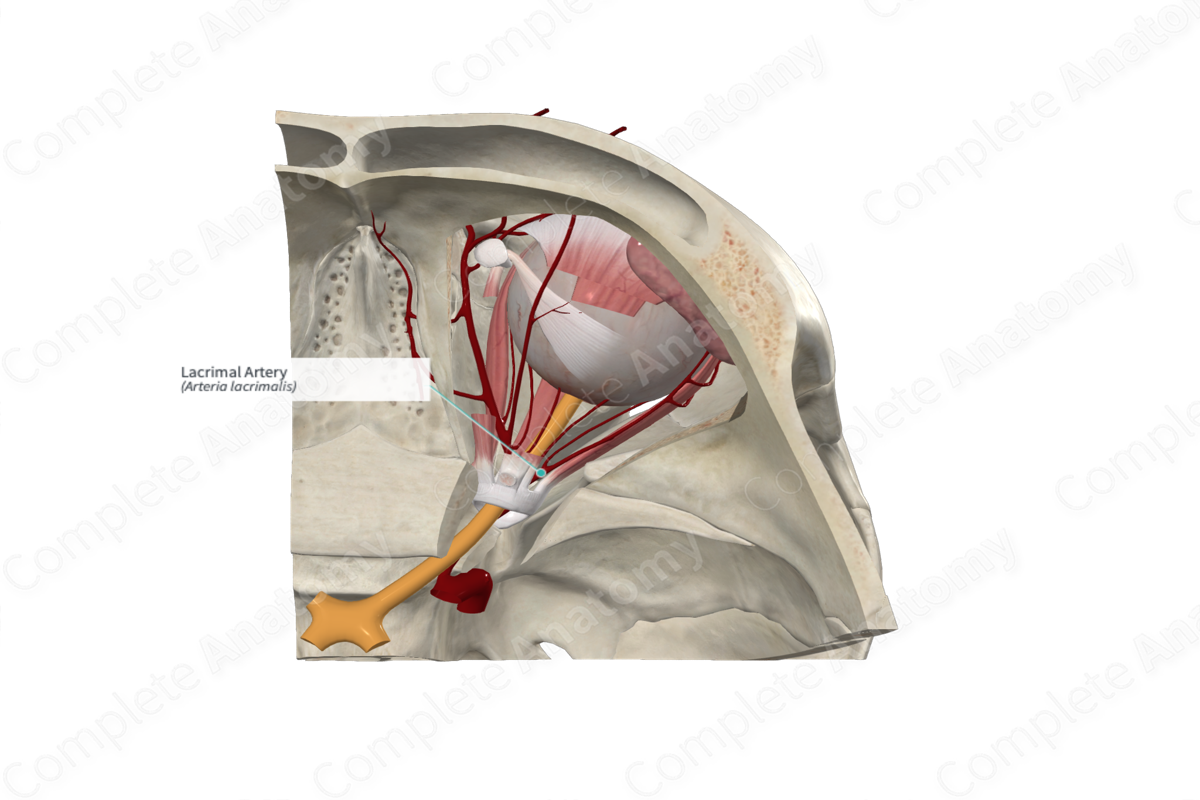
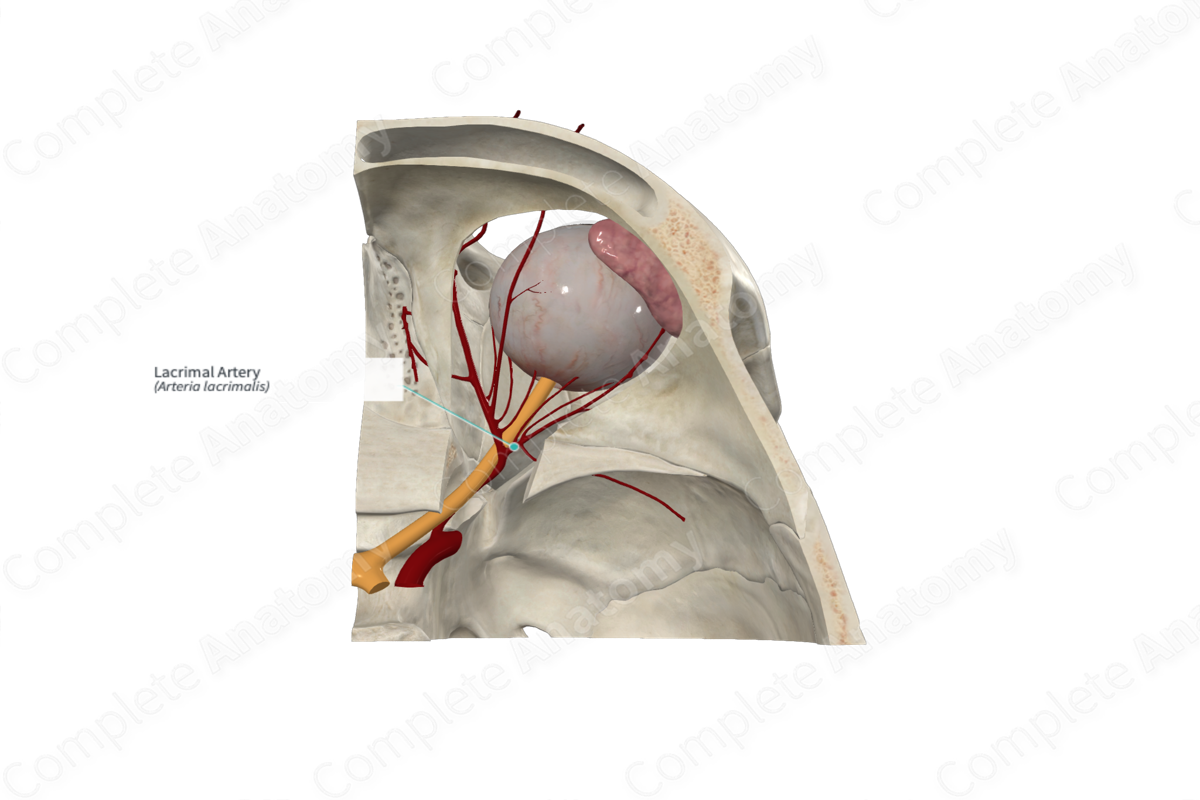
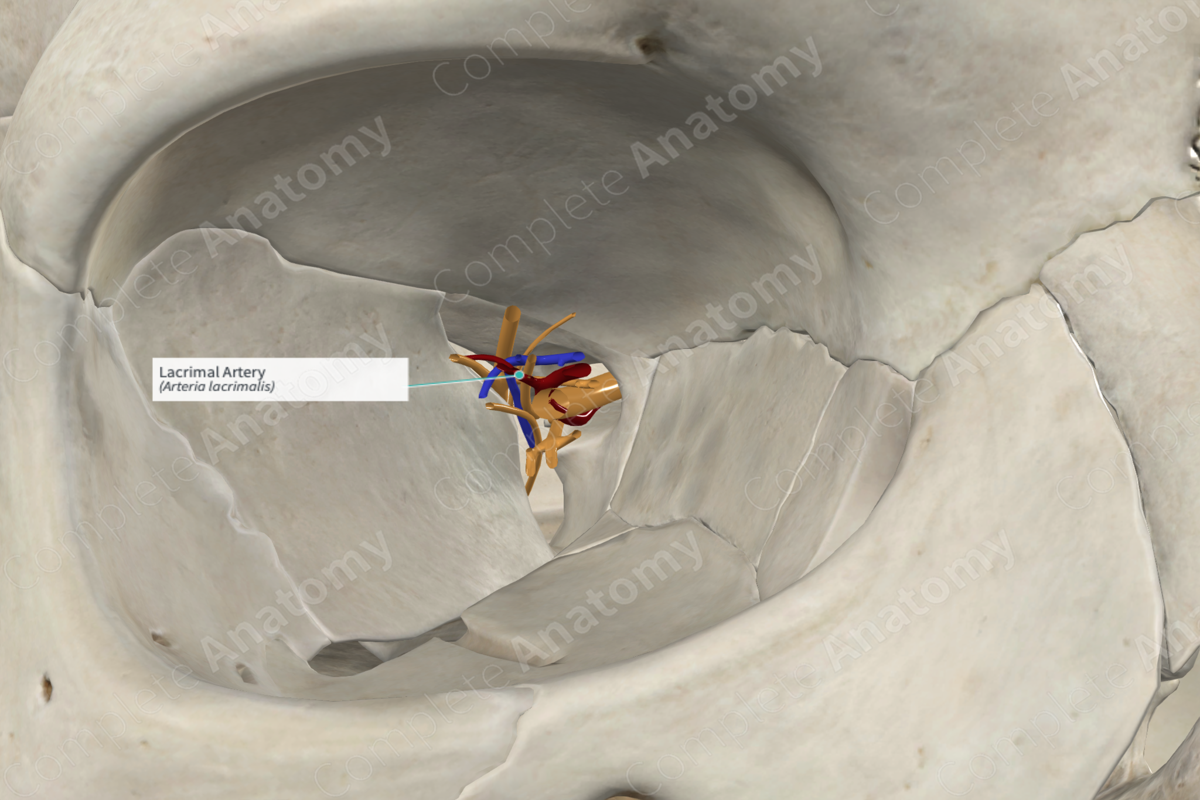
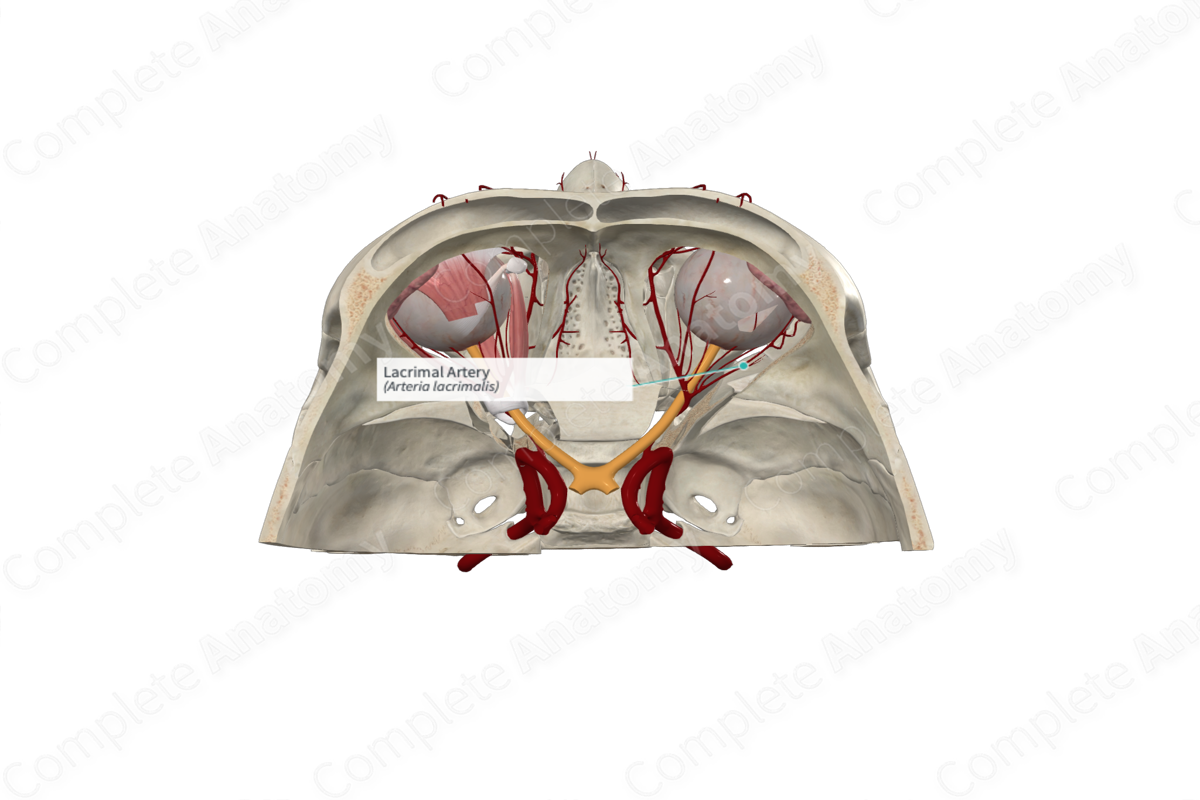
Origin: Ophthalmic artery.
Course: Traverses anteriorly in the orbital cavity above the lateral rectus muscle.
Branches: Lateral palpebral arteries, anastomotic branch with middle meningeal artery.
Supplied Structures: Lacrimal gland, superior and inferior eyelids, and conjunctiva.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The lacrimal artery is one of the largest branches arising from the ophthalmic artery. It usually arises within the orbital cavity, close to the optic foramen. However, occasionally, it may arise before the ophthalmic artery enters the orbital cavity.
Course
The lacrimal artery accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the superior surface of the lateral rectus muscle to reach the lacrimal gland. Here, it supplies the gland. It ends in the conjunctiva and the lateral sides of both the upper and lower eyelids and the lateral palpebral arteries.
Branches
After the lacrimal artery reaches the lacrimal gland, it continues anteriorly as the lateral palpebral arteries, which supply the eyelids and conjunctiva.
The lacrimal artery gives off an anastomotic branch with the middle meningeal artery. This recurrent meningeal branch passes backwards through the lateral aspect of the superior orbital fissure to anastomose with a branch of the middle meningeal artery (Dorland, 2011).
Supplied Structures
The lacrimal artery provides a blood supply primarily to the lacrimal gland. Indirectly, it supplies the eyelids and conjunctiva via the lateral palpebral arteries.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products