Description
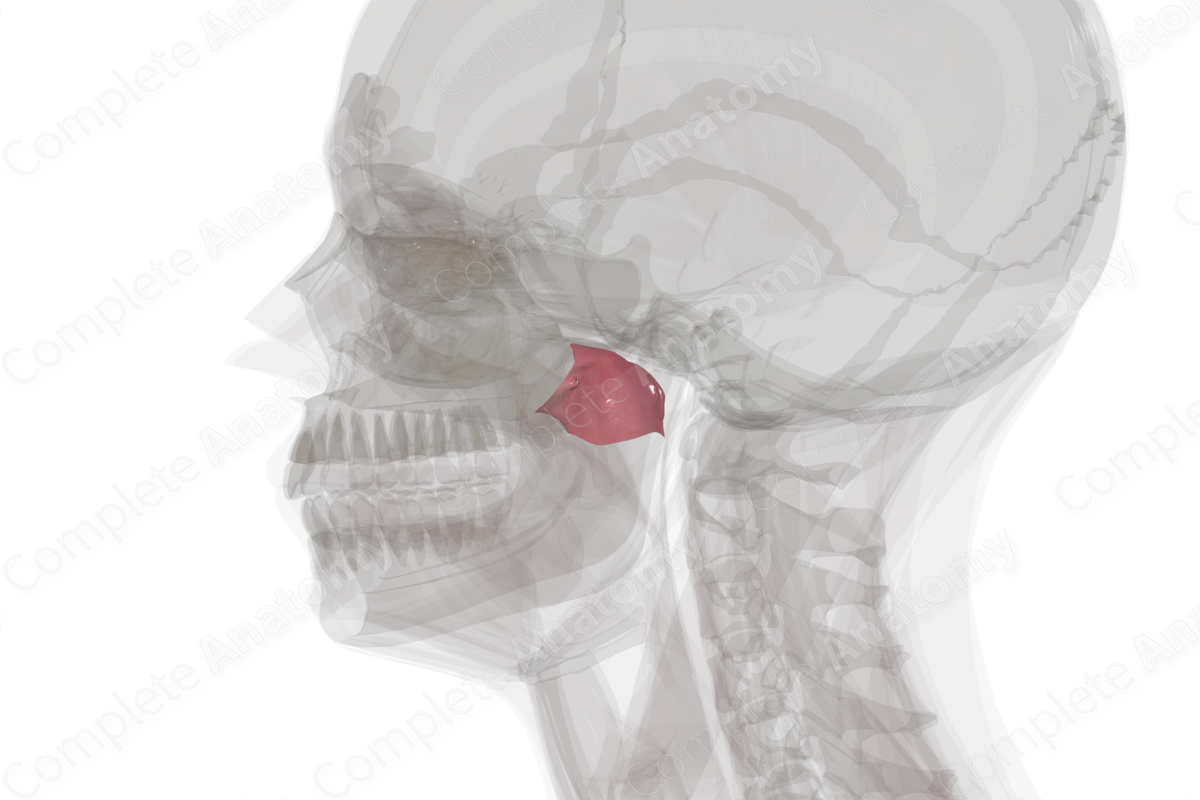
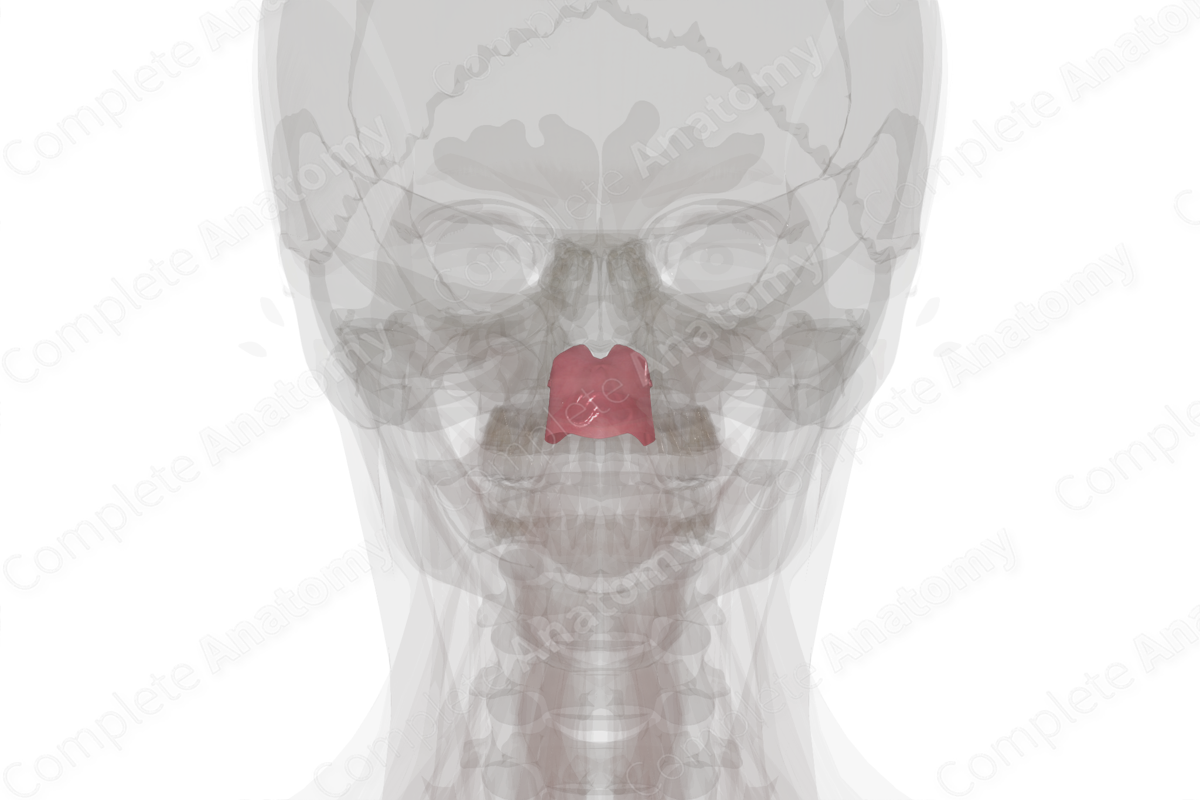
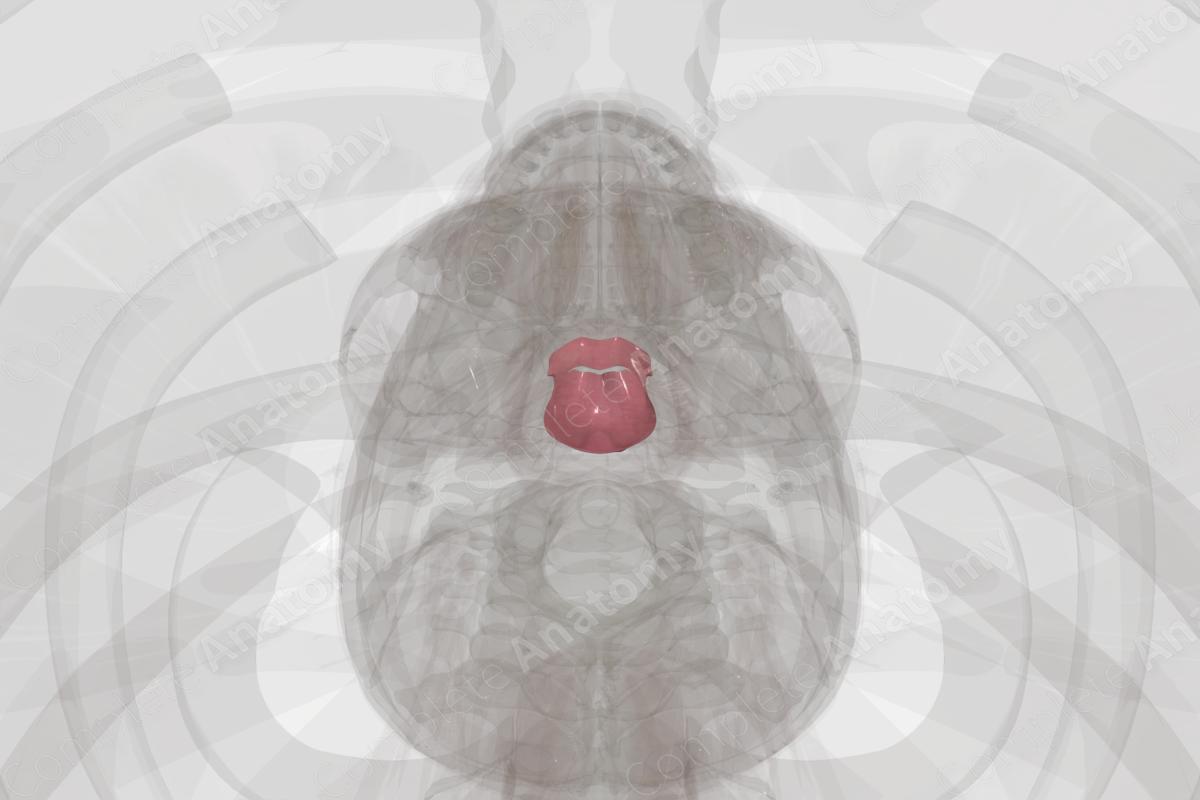
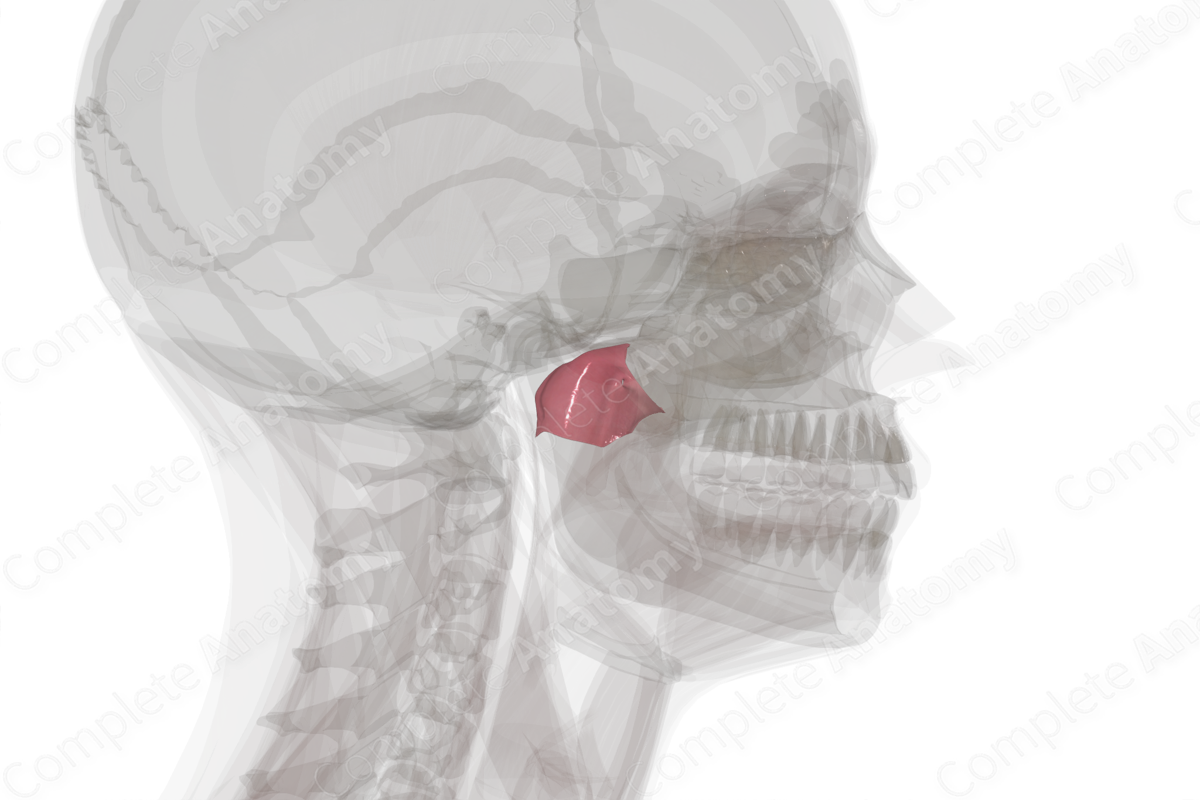
The nasopharynx begins at the posterior aspect of the nasal cavity. It extends in a posteroinferior manner to the uvula of the soft palate where it is continuous with the oropharynx. A portion of the sphenoid bone forms the roof of the nasopharynx. The soft palate forms the floor of the nasopharynx. The lateral walls of the nasopharynx are formed from nasopharyngeal mucosa. Underlying the mucosa is the pharyngobasilar fascia and the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
The auditory tube (also known as the pharyngotympanic or the Eustachian tube) opens into the nasopharynx. The mucosal lining of the pharynx is continuous with the auditory tube and, thus, infections may spread from the oral or nasal cavities to the ear.
A mucosal fold forms around the opening of the auditory tube called the torus tubarius. It extends inferiorly as the salpingopharyngeal fold that covers the salpingopharyngeus muscle.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products