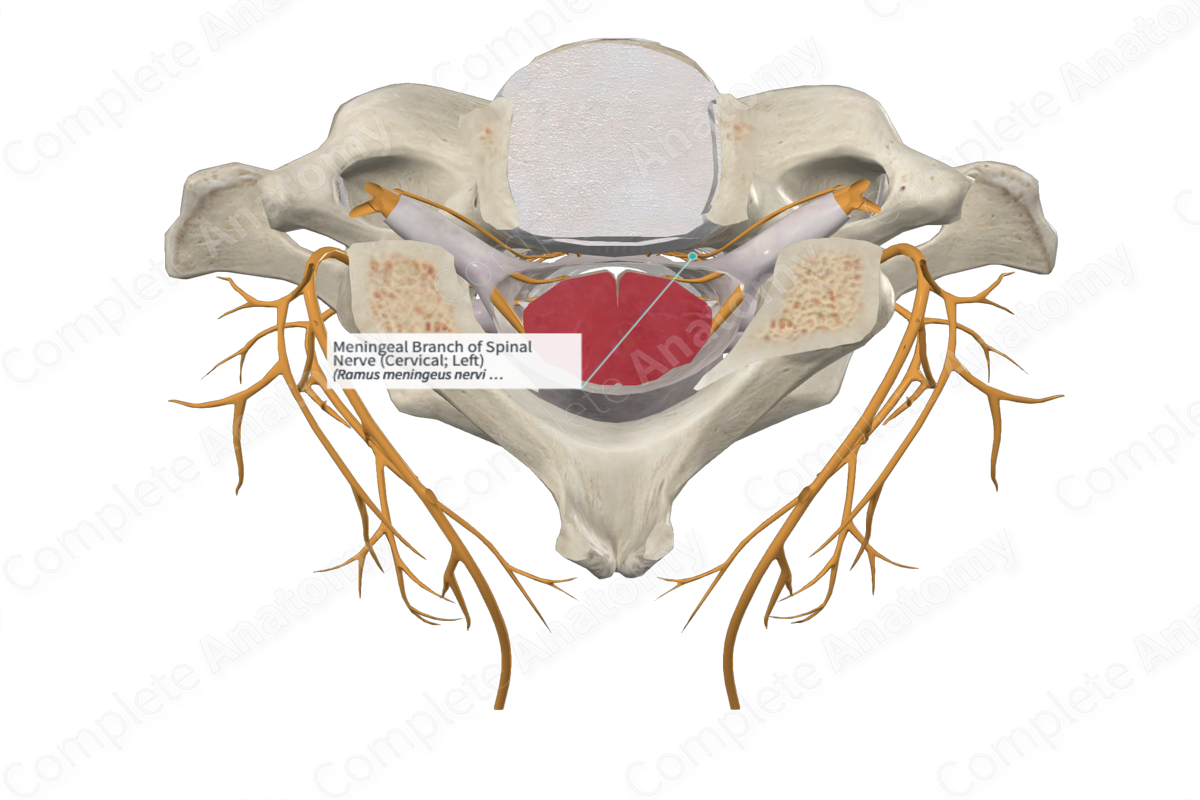
Meningeal Branch of Spinal Nerve (Cervical; Right)
Ramus meningeus nervi spinalis
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Anterior ramus of spinal nerves.
Course: Passes backwards into the vertebral canal.
Branches: Ascending, descending, and transverse branches.
Supply: Posterior longitudinal ligament, vertebral bodies, intervertebral discs, ventral surface of the dural sac, dura mater along the clivus, and the atlantoaxial joint.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The meningeal branches occur at all vertebral levels and originate directly from the anterior rami of the spinal nerves, with contributions from the gray communicating branches (gray rami communicantes), except at cervical levels C1-C5. Therefore, most of the meningeal branches contain sensory and sympathetic fibers. The meningeal branches at C6 and C7 spinal levels receive contributions from the vertebral nerve.
Course
Each meningeal branch passes backwards (recurrent pathway) from their origin through the intervertebral foramen to enter the vertebral canal. These branches will form a plexus on the ventral surface of the dural sac as well as provide innervation to the vertebral column ventral to the dural sac.
Branches
Each meningeal branch has ascending, descending, and transverse branches. Each of these branches communicates with the corresponding branches above, below, and from the opposite side of the body.
Supplied Structures
The meningeal branches supply the ventral surface of the dural sac, the posterior longitudinal ligament, periosteum of the vertebral bodies, posterior aspect of intervertebral discs, dura mater along the clivus, and the atlantoaxial joint.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




