Quick Facts
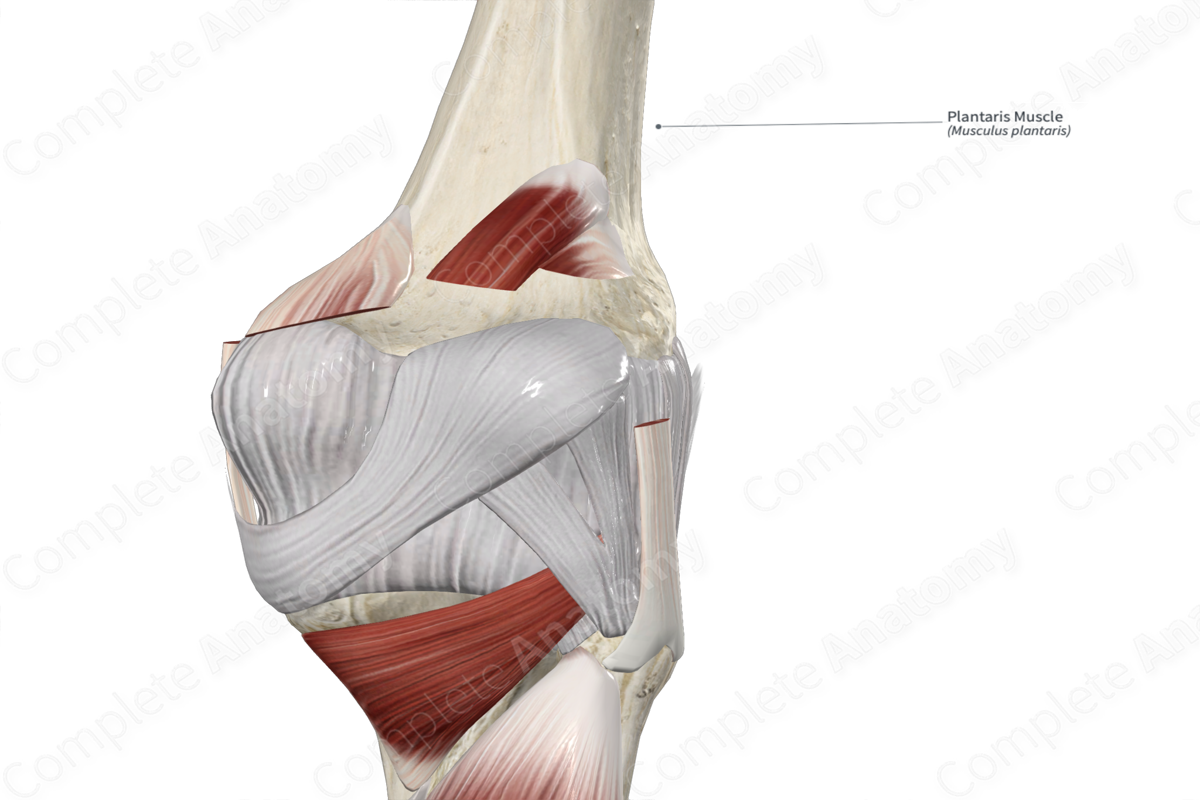
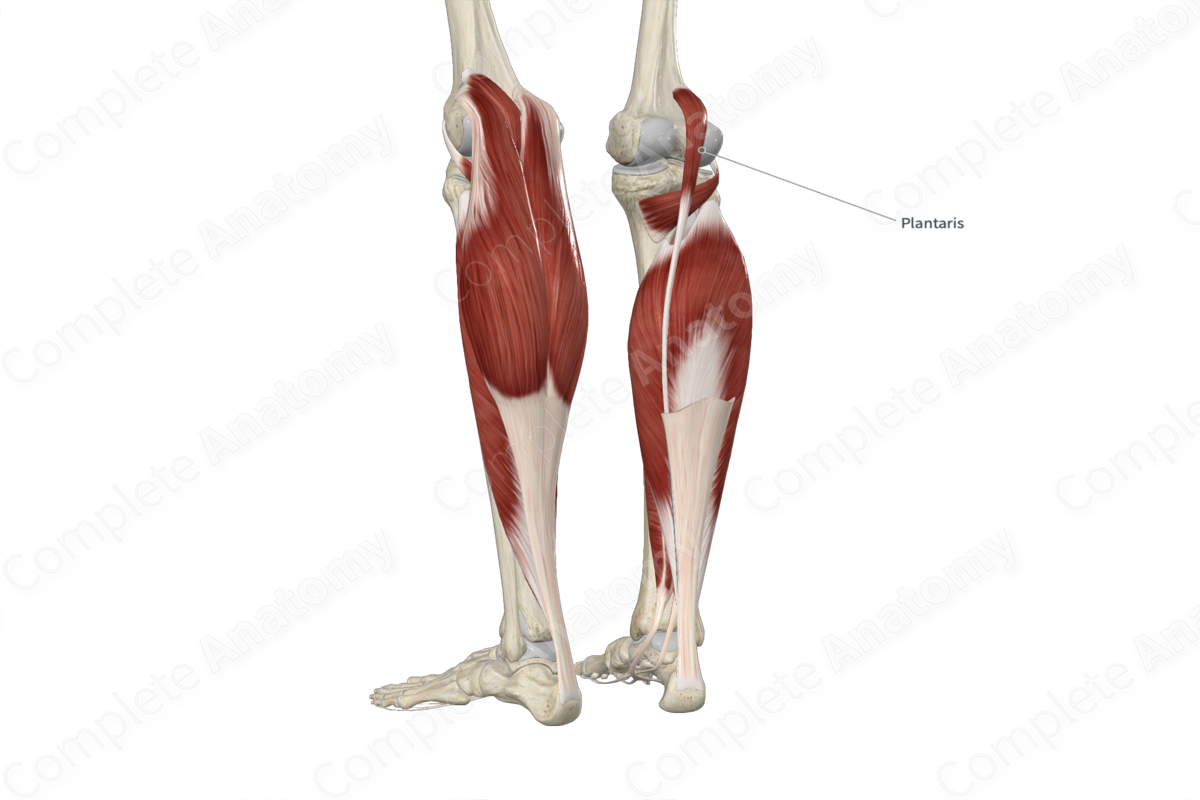
Origin: Lateral supracondylar line of femur.
Insertion: Posterior surface of calcaneus.
Action: Assists in plantarflexion of foot at ankle joint; assists in flexion of leg at knee joint.
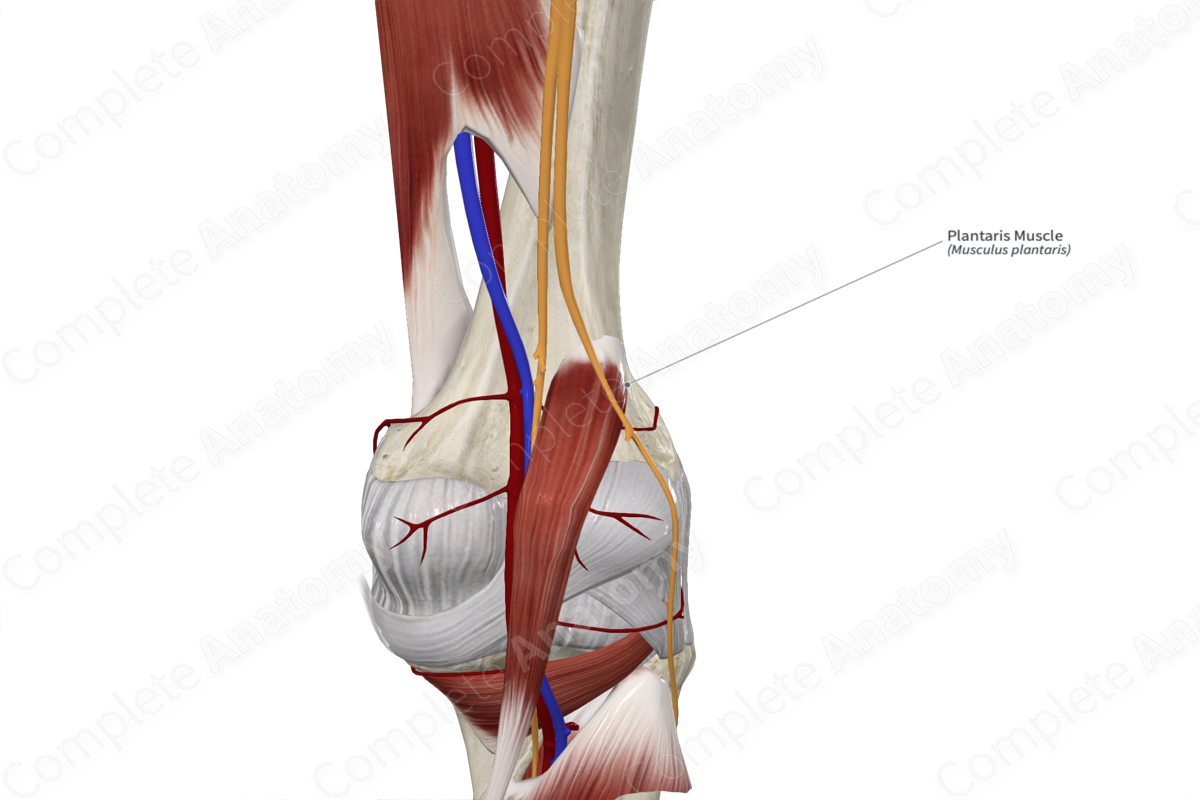
Innervation: Tibial nerve (S1-S2).
Arterial Supply: Sural, popliteal, and superior lateral genicular arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The plantaris muscle originates from the:
- inferior half of the lateral supracondylar line of femur;
- oblique popliteal ligament.
Insertion
The fibers of the plantaris muscle travel inferomedially and insert, via a long, narrow tendon, onto the posterior surface of calcaneus either:
- directly, where the tendon of plantaris attaches to the calcaneus, medial to the calcaneal tendon;
- indirectly, where the tendon of plantaris merges with the calcaneal tendon, which attaches to the calcaneus.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
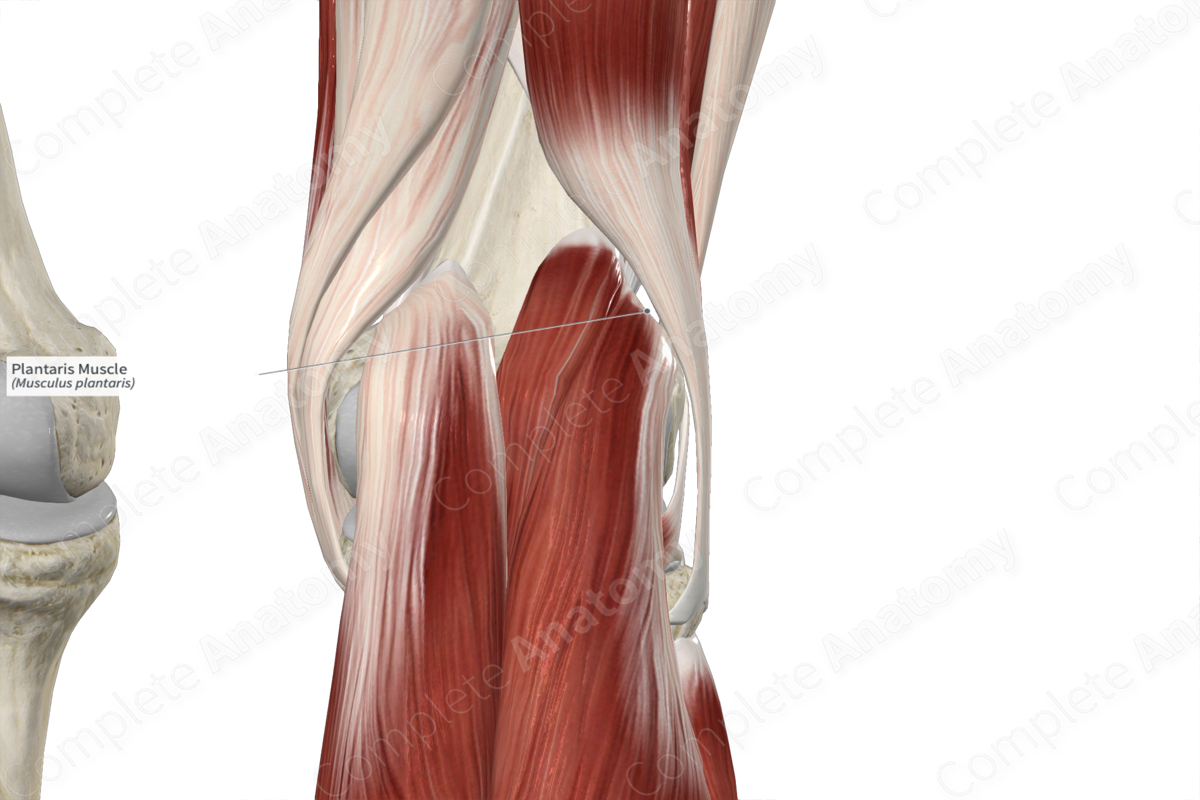
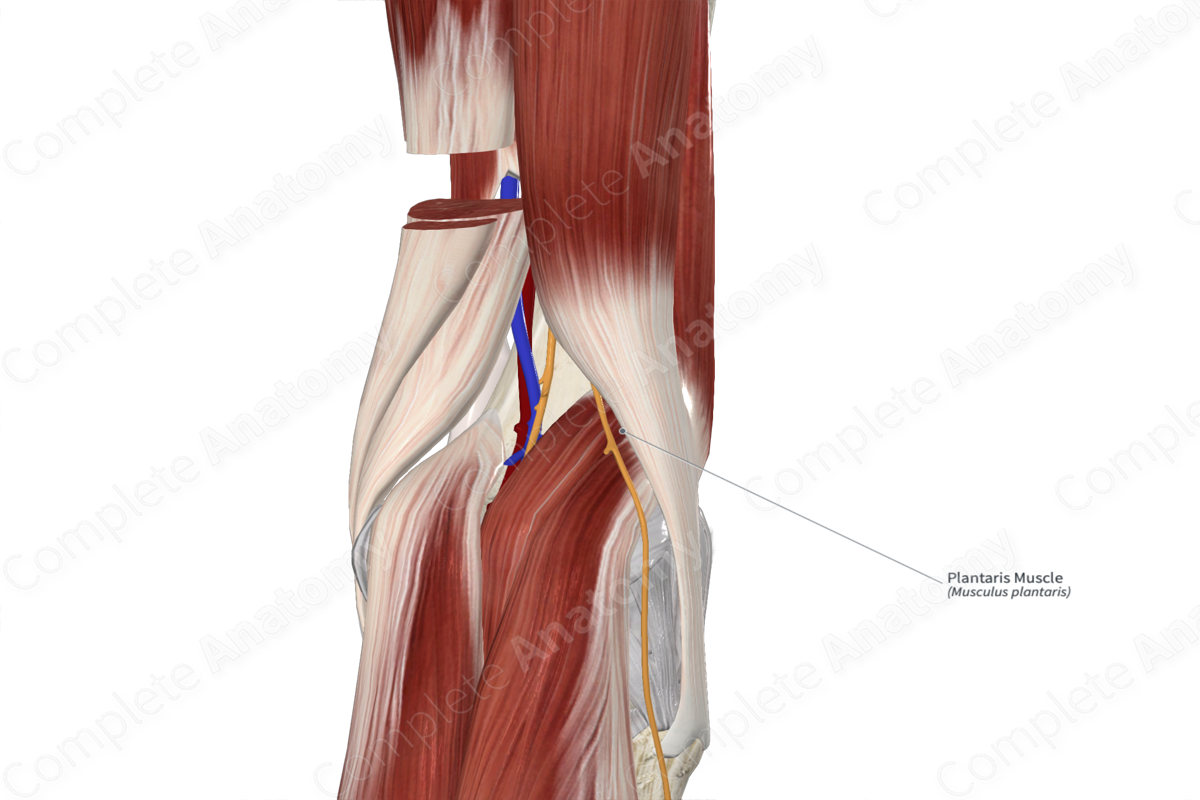
The plantaris muscle is one of the muscles of the superficial part of the posterior compartment of the leg. It is a long, narrow, fusiform skeletal muscle.
It is located:
- anterior (deep) to the medial head of gastrocnemius muscle and the calcaneal tendon;
- posterior (superficial) to the femur and tibia, the capsule of the knee joint, the ankle joint, and the popliteus and soleus muscles;
- medial to the lateral head of gastrocnemius muscle.
Actions
The plantaris muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- assists in plantarflexion of the foot at the ankle joint;
- assists in flexion of the leg at the knee joint (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Plantaris tendon grafts
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Actions
The plantaris muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- assists in plantarflexion of the foot at the ankle joint;
- assists in flexion of the leg at the knee joint (Standring, 2016).
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products