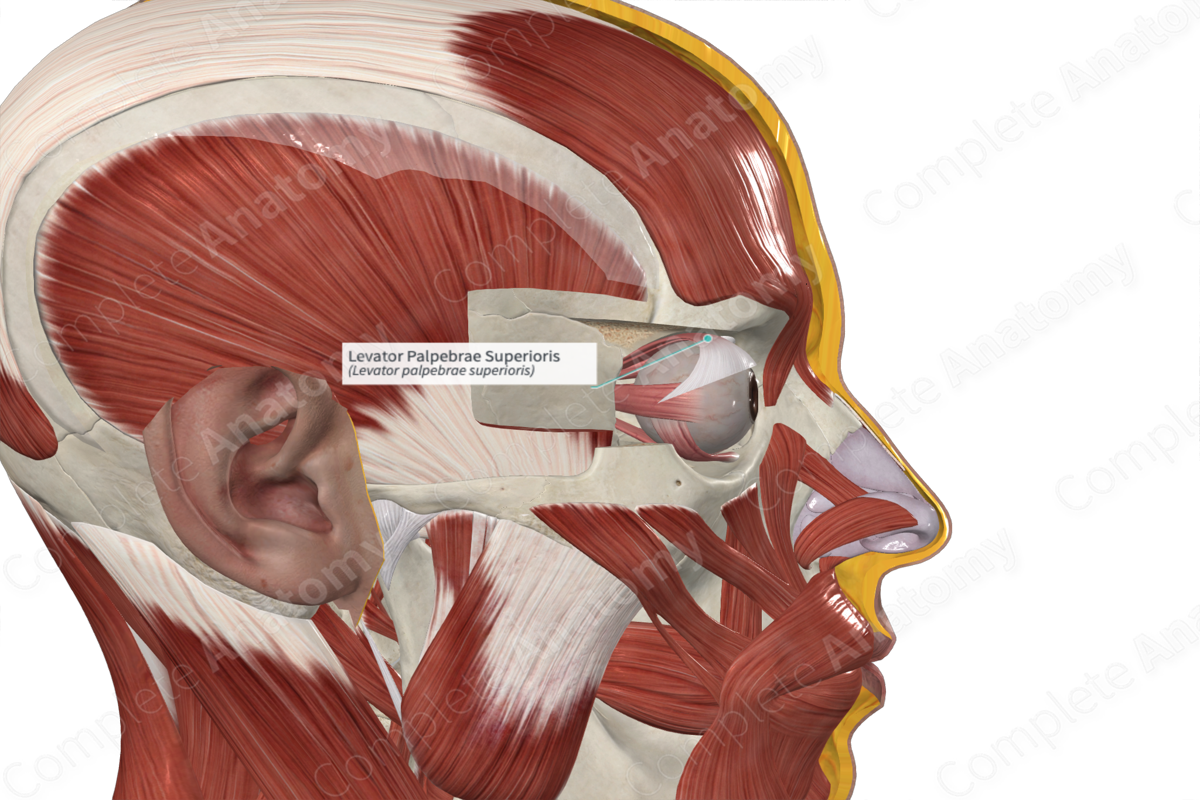
Quick Facts
Origin: Lesser wing of sphenoid bone.
Insertion: Superior tarsus and skin of upper eyelid.
Action: Elevates upper eyelid.
Innervation: Superior branch of oculomotor nerve (CN III).
Arterial Supply: Ophthalmic and supraorbital artery.
Origin
The levator palpebrae superioris muscle arises from the inferior part of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, superior to the optic canal.
Insertion
From its origin, the levator palpebrae superioris extends anteriorly, above the superior rectus muscle. As it extends forward, the muscle broadens and becomes aponeurotic at its anterior end. The deeper aponeurotic fibers attach to the anterior surface of the superior tarsus in the upper eyelid. These fibers are accompanied by smooth muscle fibers, the superior tarsal muscle. The remaining superficial fibers radiate to pass through the orbicularis oculi muscle and attach to the skin of the upper eyelid.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The adjoining connective tissue sheaths of levator palpebrae superioris and superior rectus fuse. Where they split to access their distal attachments is where the superior conjunctival fornix is located.
Actions
The levator palpebrae superioris muscle elevates the upper eyelid. It works in opposition to the palpebral part of the orbicularis oculi muscle, which is responsible for closing the eyelids.
Additionally, the levator palpebrae superioris is linked to the superior rectus muscle via a check ligament. Therefore, when the superior rectus muscle contracts and gaze is directed upwards, the upper eyelid is also elevated.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Ptosis
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




