Quick Facts
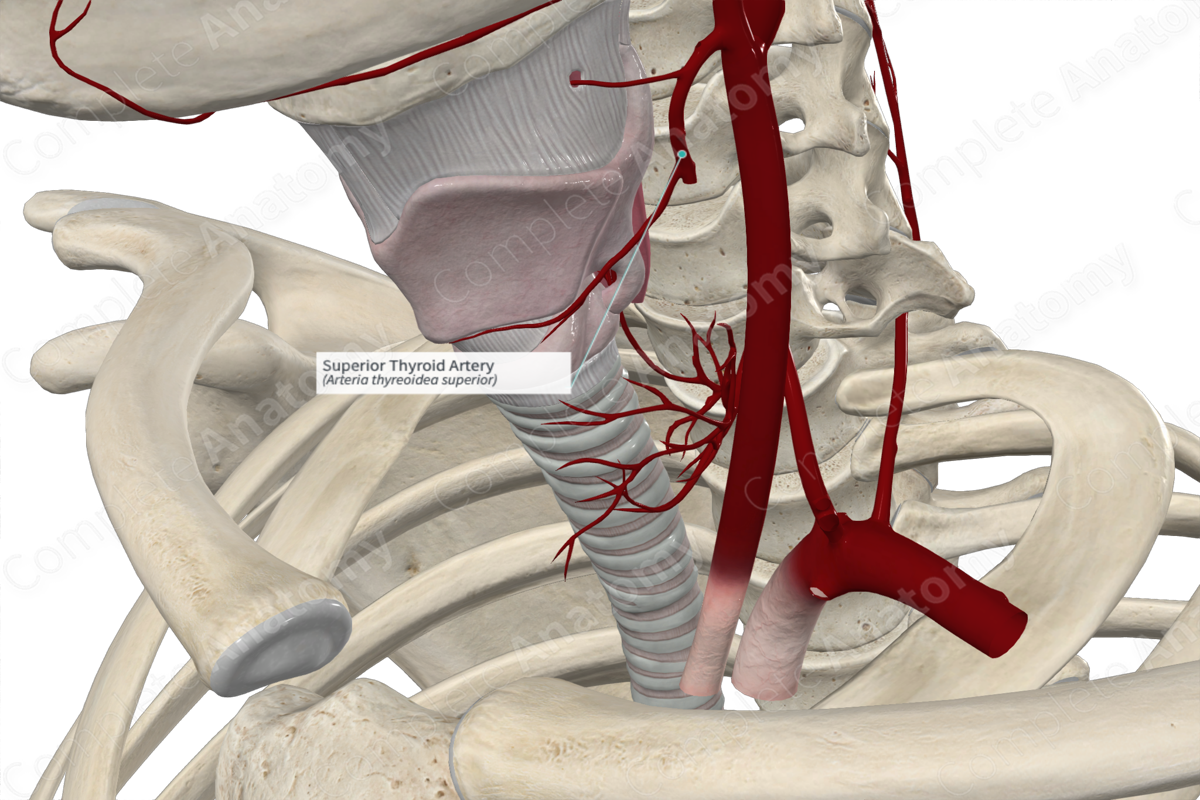
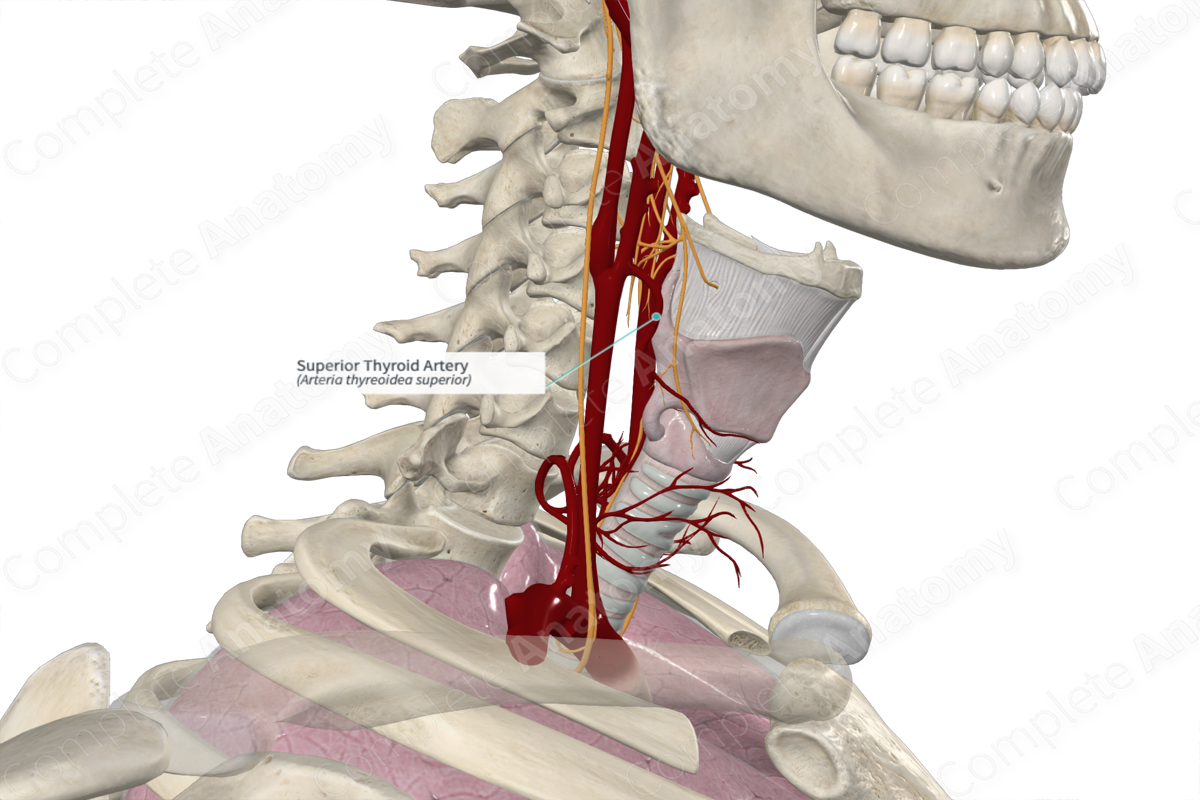
Origin: External carotid artery.
Course: Descends from the anterior surface of the external carotid artery.
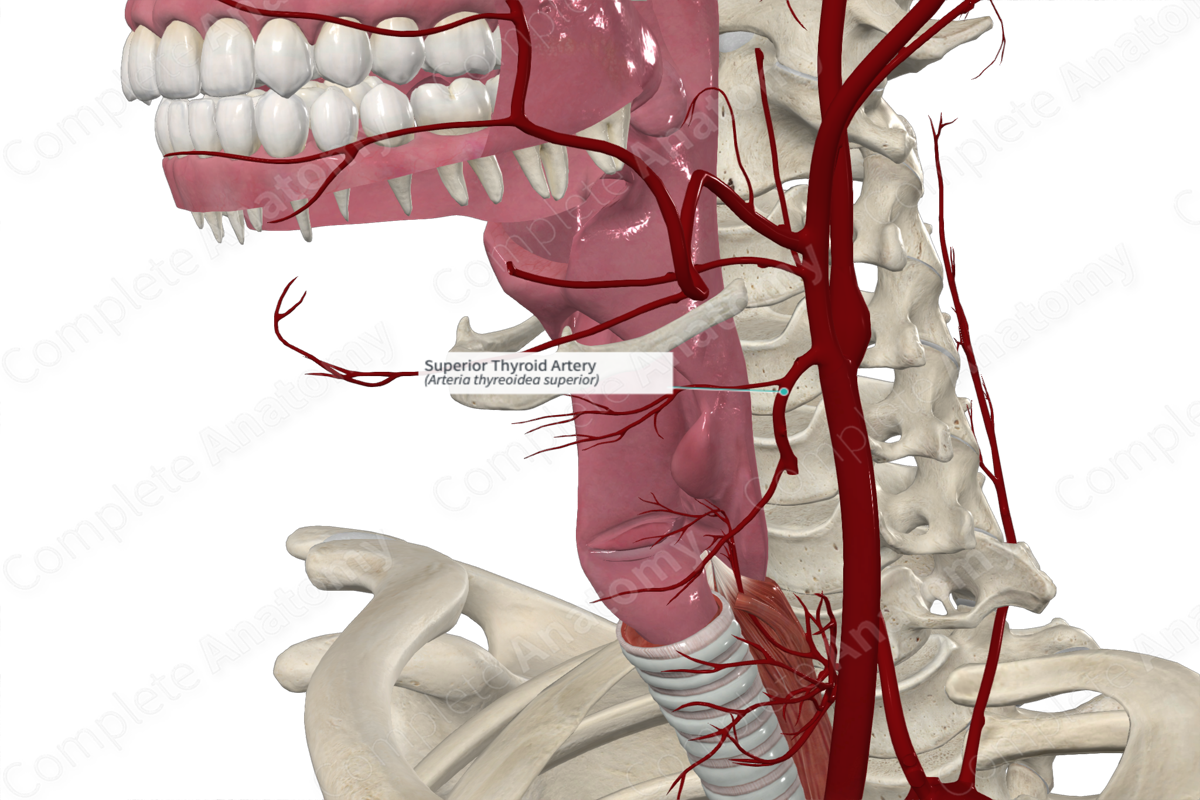
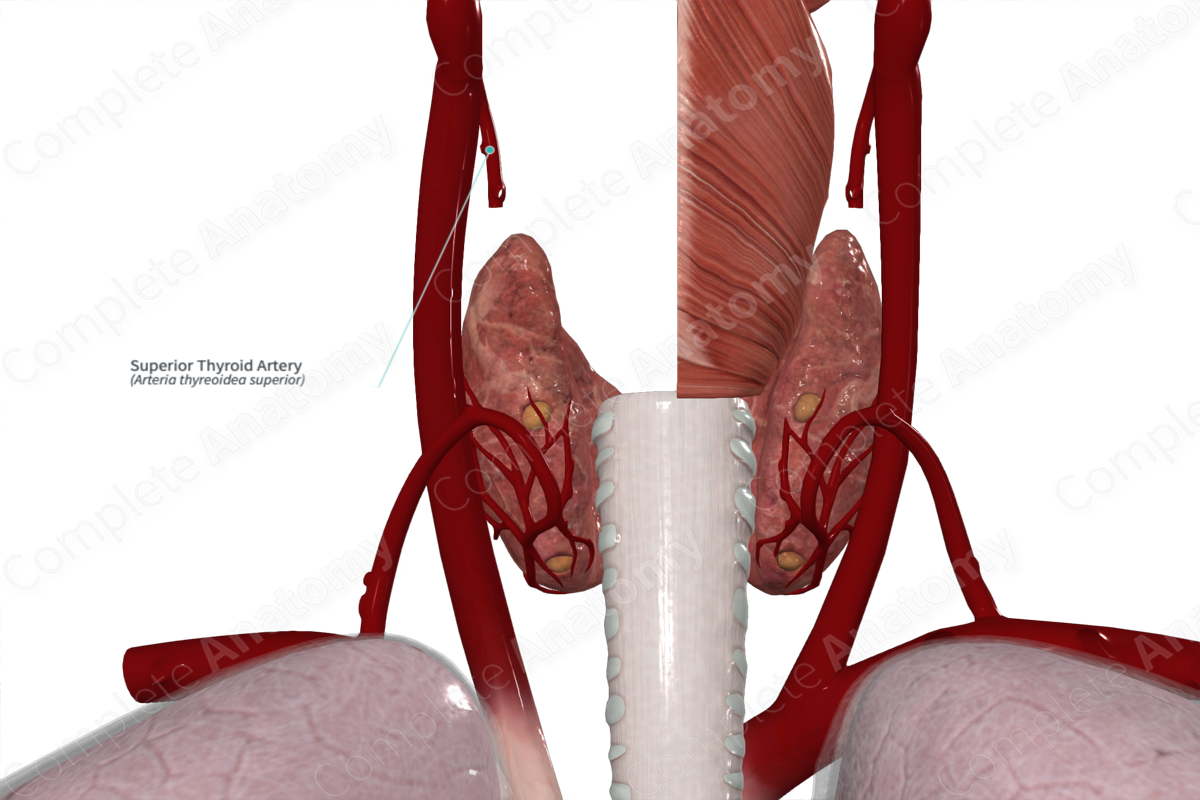
Branches: Superior laryngeal artery, sternocleidomastoid, cricothyroid, infrahyoid, and anterior, posterior, and lateral glandular branches.
Supplied Structures: Sternocleidomastoid, cricothyroid, and infrahyoid strap muscles, thyroid gland, and tissue of the upper part of the larynx.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The superior thyroid artery usually arises as the first branch of the external carotid artery, just inferior to the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. However, the superior thyroid artery may arise from the division of the common carotid artery, from the subclavian artery, or share a common trunk with the lingual and facial arteries (Tubbs et al, 2016).
Course
The superior thyroid artery descends from the anterior surface of the external carotid artery along the lateral border of the thyrohyoid muscle. It extends towards the apex of the lobe of the thyroid gland.
Branches
The superior thyroid artery gives rise to several branches, including the superior laryngeal artery, which pierces through the thyrohyoid membrane to enter the larynx.
It also gives rise to muscular branches including the sternocleidomastoid, cricothyroid, and infrahyoid branches. Finally, it gives rise to several glandular branches.
Supplied Structures
The superior thyroid artery supplies the upper part of the larynx via the superior laryngeal artery. It also supplies the sternocleidomastoid, cricothyroid, and infrahyoid strap muscles via its muscular branches. The glandular branches of the superior thyroid artery provide an extensive blood supply to the thyroid gland.
References
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. & Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products