Quick Facts
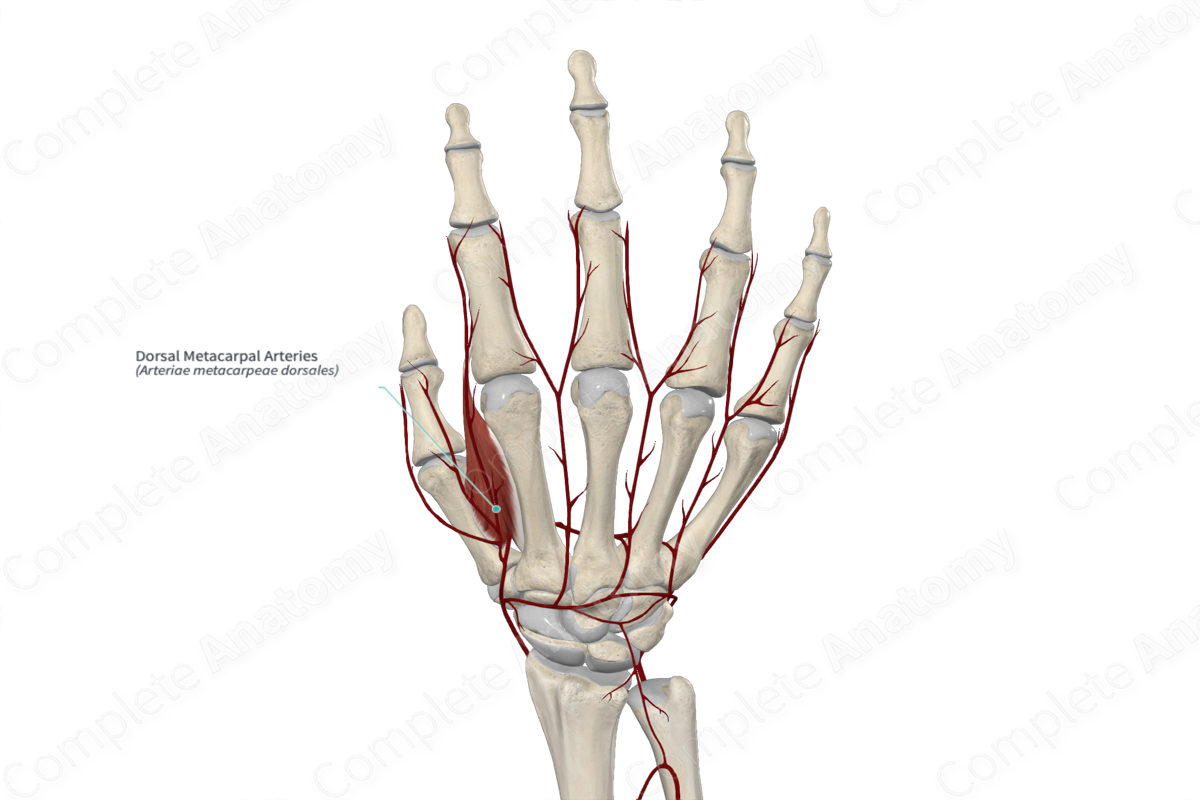
Origin: The first dorsal metacarpal artery arises from the radial artery; the second, third, and fourth arise from the dorsal carpal anastomosis.
Course: Distally, along dorsum of the metacarpals.
Branches: Dorsal digital arteries.
Supplied Structures: Dorsum of hand and digits.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
There are four dorsal metacarpal arteries which are numbered from one to four. The first dorsal metacarpal artery originates from the radial artery. The remaining dorsal metacarpal arteries originate from the dorsal carpal anastomosis (or arch).
Course
The first dorsal metacarpal artery originates once the radial artery pierces the two heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscle. It then bifurcates, whereby one branch courses distally on the medial aspect of the thumb and the other courses along the lateral aspect of the second digit.
The remaining second, third, and fourth dorsal metacarpal arteries run distally from the dorsal carpal anastomosis along the dorsal aspect of the dorsal interossei muscles.
Branches
The dorsal metacarpal arteries terminally bifurcate at the level of distal metacarpal head. Here they form the dorsal digital arteries. The dorsal metacarpal arteries anastomose with the deep palmar arch via perforating arteries
Supplied Structures
The dorsal metacarpal arteries supply to the dorsal aspect of the hand and the digits.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products