Quick Facts
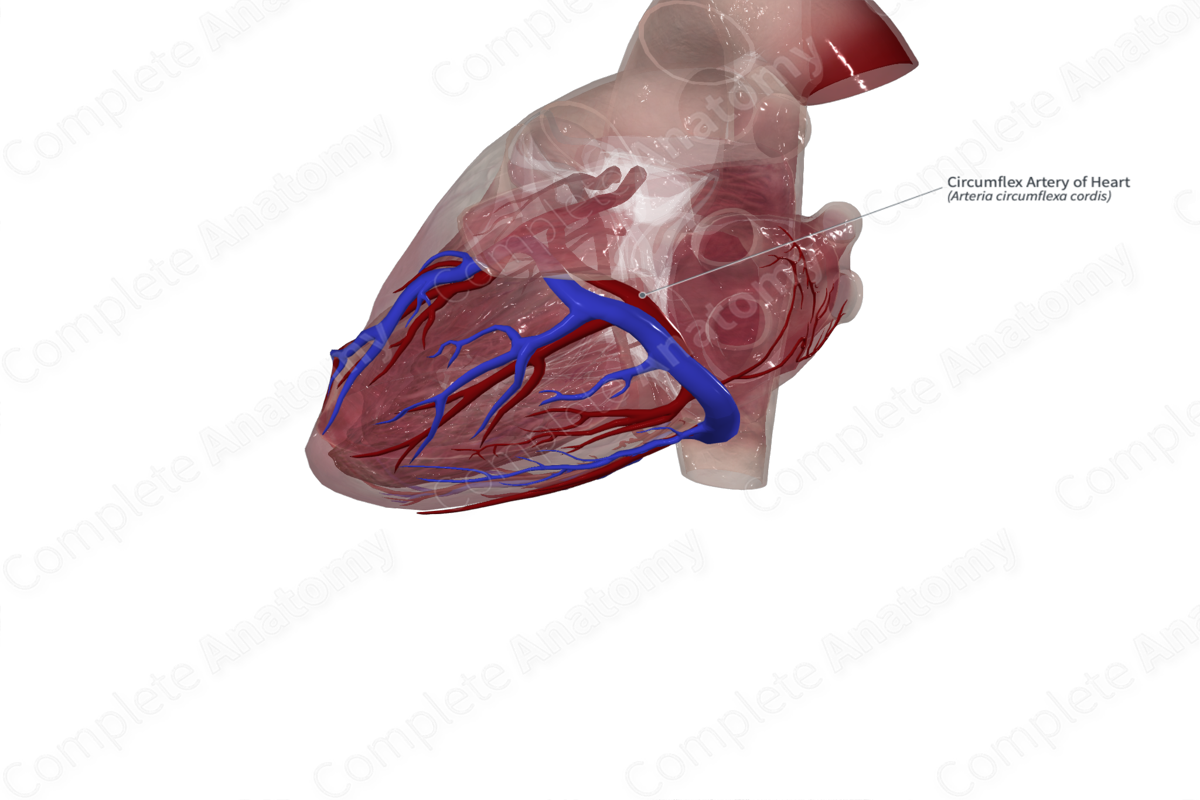
Origin: Left coronary artery.
Course: Within coronary sulcus from anterior to posterior aspect of the heart.
Branches: Atrial, left marginal, and posterior left ventricular branches.
Supplied Structures: Left atrium and ventricle.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
There are two main branches of the left coronary artery. These are the circumflex and the anterior interventricular branches.
Course
The circumflex artery travels along the anterior aspect of the heart, within the atrioventricular groove. Here, the left atrial appendage sits over the vessel anteriorly. As the name suggests, the circumflex branch curves to the left and becomes posterior, still within the atrioventricular groove. It continues as far as “the crux” and gives off the posterior interventricular artery in hearts with left coronary dominance (Standring, 2016).
Branches
The branches of the circumflex artery include the left marginal and anterior ventricular branches, which run parallel to the diagonal artery. The artery to the sinuatrial node may arise from the anterior portion of the circumflex artery. The artery to the atrioventricular node arises near the crux in 20% of individuals as a branch of the posterior interventricular artery when left dominance occurs (Standring, 2016). The posterior left ventricular branches in this case are diminished.
Supplied Structures
The circumflex branch contributes to the supply of the left atrium and ventricle.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary atherosclerosis
- Coronary bypass graft
- Coronary angioplasty
- Coronary occlusion
- Coronary revascularization
- Coronary artery fistula
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





