Quick Facts
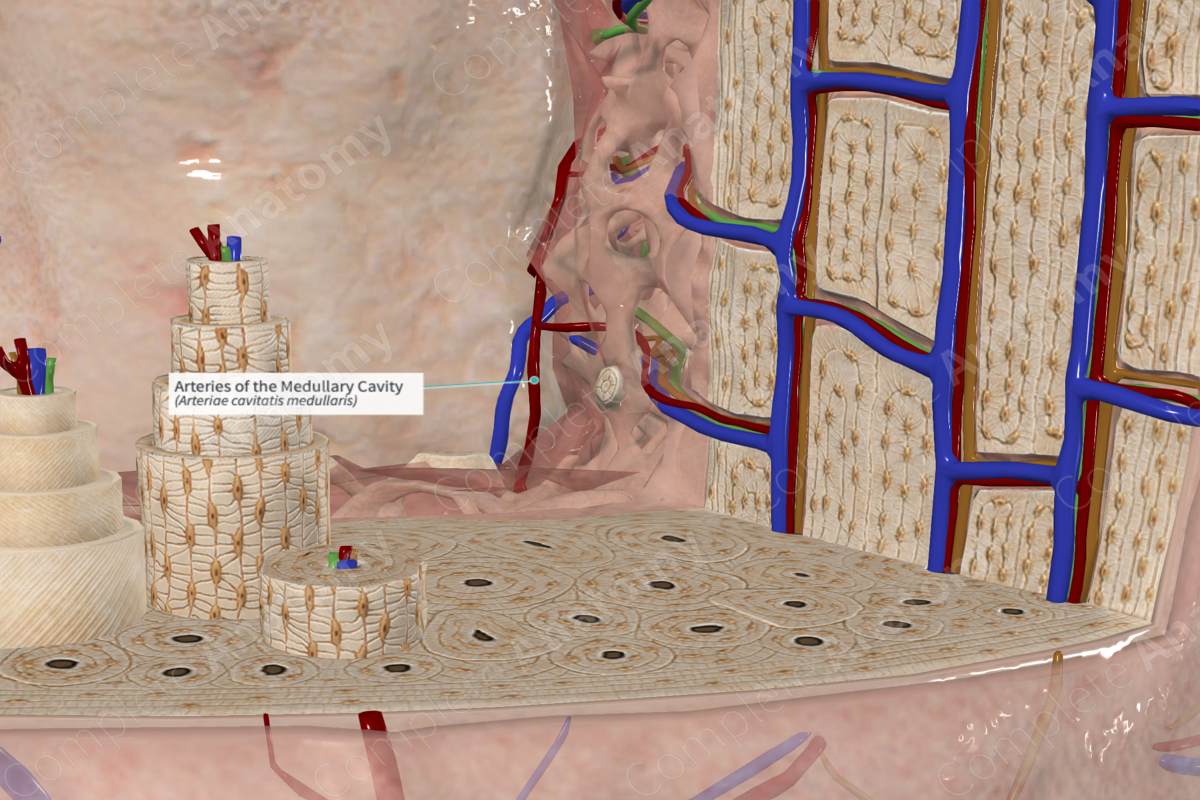
The nutrient artery supplies the medullary cavity.
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure/Morphology
The medullary arteries are derived from several external vessels. The epiphysis, metaphysis and diaphysis contain several openings in the bone to permit the passage of blood vessels into the medullary cavity. Within the cavity these vessels branch and anastomose to provide a continuous vascular supply to the entire bone.
In the diaphysis of long bones, the shaft is supplied by the nutrient artery. If you examine the outer cortical surface of long bones, there is normally a singular nutrient foramen in its diaphysis. This marks the entry point of the nutrient artery as it courses towards the medullary cavity in a passageway called the nutrient canal. The nutrient artery does not branch within the nutrient canal, but upon entry to the medullary cavity, it bifurcates into ascending and descending branches (Standring, 2016). The branches travel to the outer limits of the shaft and anastomose with the epiphyseal and metaphyseal vascular supply.
Anatomical Relations
The medullary arteries within the shaft form a rich vascular network that forms the medullary sinusoids associated that drain into a central venous sinus. Other branches of the medullary arteries travel towards the cortex. As the blood flow is traveling from the innermost cavity outward, it is called centrifugal blood flow. In the cortex it courses through the perforating canals to supply the nutrient canals of the osteon.
Function
The medullary arteries form a rich vascular supply for the inner medullary cavity, the spongy bone and also the inner two thirds of cortical bone.
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series: Elsevier Limited.
