Description
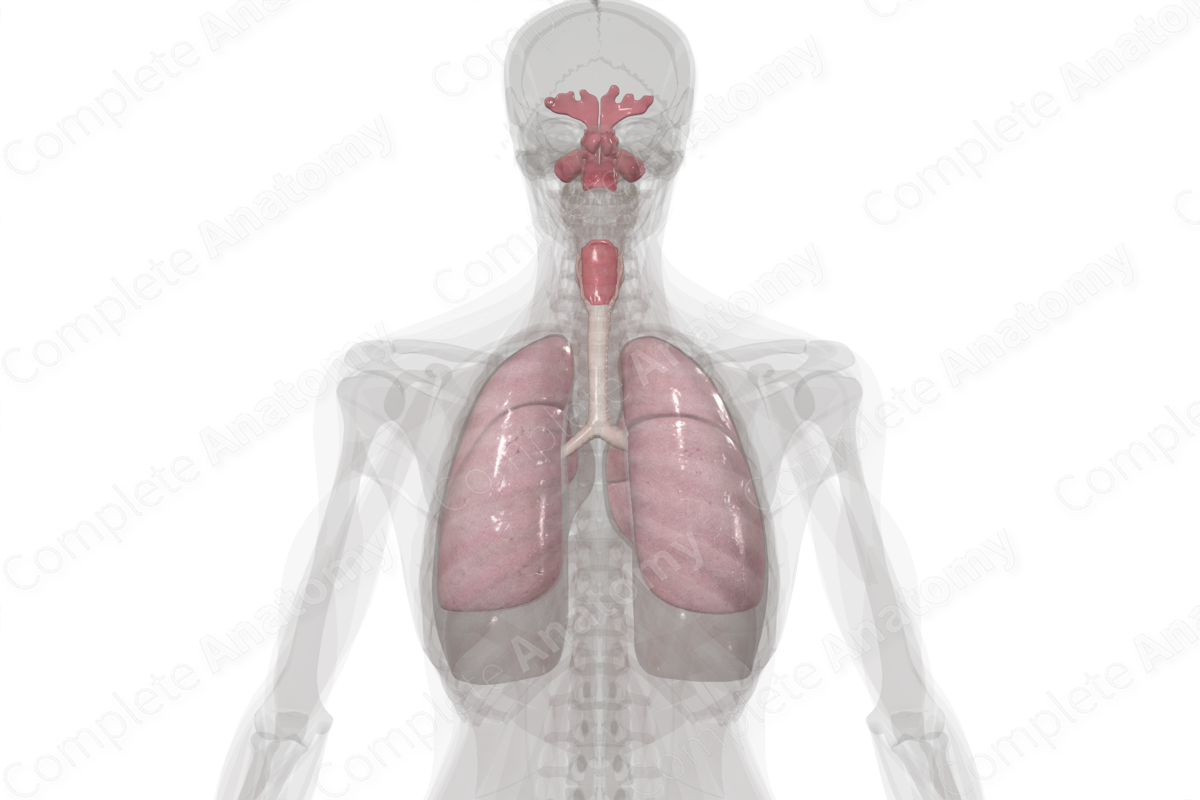
The respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange with the external environment. Anatomically, the respiratory system is divided into two distinct parts; the upper respiratory system and the lower respiratory system.
The upper respiratory system (or upper respiratory tract) consists of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, and larynx. In addition to respiration, the upper respiratory system is also involved in phonation (i.e., the production of vocal sounds), mainly via the movement of air across the vocal cords.
The lower respiratory system (or lower respiratory tract) consists of the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, and lungs. This is the extensively branched region of the respiratory system. It appears like an inverted tree, with the trachea representing its trunk, the bronchi and bronchioles representing its branches, and the alveoli representing its leaves. These sac-like endings (i.e., alveoli) are in close contact with the blood vessels. It is in the alveoli that gaseous exchange occurs whereby oxygen enters and carbon dioxide exits the blood vessels.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Respiratory system anatomy and physiology: Video, Causes, & Meaning
Respiratory system anatomy and physiology: Symptoms, Causes, Videos & Quizzes | Learn Fast for Better Retention!