Quick Facts
Origin: Ulnar nerve.
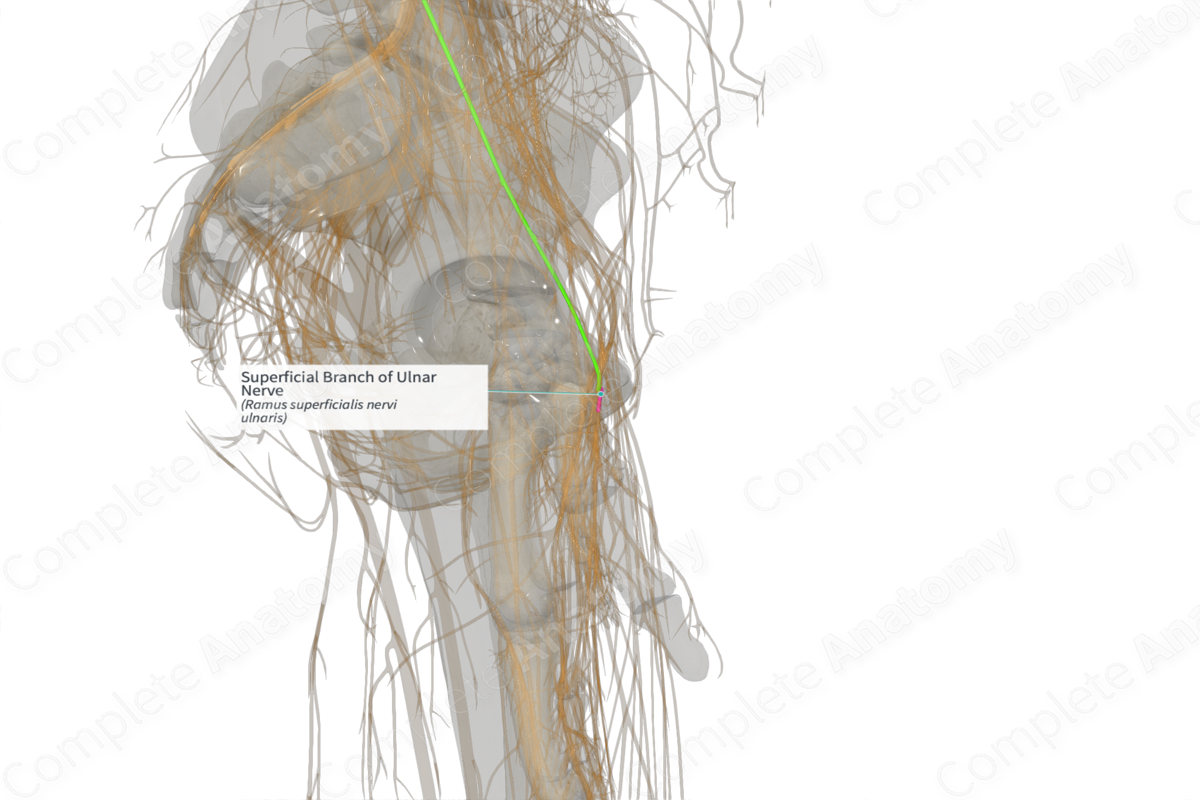
Course: The ulnar nerve crosses over the flexor retinaculum to divide into superficial and deep terminal branches. The superficial branch innervates palmaris brevis and becomes cutaneous to palmar aspect of medial one and half fingers.
Branches: Common Palmar Digital branch of ulnar nerve, muscular branch of ulnar nerve to hypothenar muscles.
Supply: Hypothenar muscles (abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, and opponens digiti muscles), palmaris brevis muscle, and skin of palmar aspect of medial one and a half digits.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The superficial branch arises as one of the two terminal branches of the ulnar nerve at the distal border of the flexor retinaculum.
Course
The ulnar nerve crosses the wrist between the tendons of flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum superficialis muscles. It divides into superficial and deep terminal branches at the distal border of the flexor retinaculum. The superficial branch supplies palmaris brevis and becomes cutaneous to provide digital branches to medial one and a half digits.
Branches
The superficial branch gives off nerve fibers to the hypothenar muscles and then becomes the common palmar digital nerve. It further subdivides into proper palmar digital nerves for innervating the skin of adjacent sides of the ring and little fingers.
Supplied Structures
The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve provides branches that innervate the hypothenar muscles (abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, and opponens digiti muscles), palmaris brevis muscle, and skin of palmar aspect of medial one and a half digits.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




