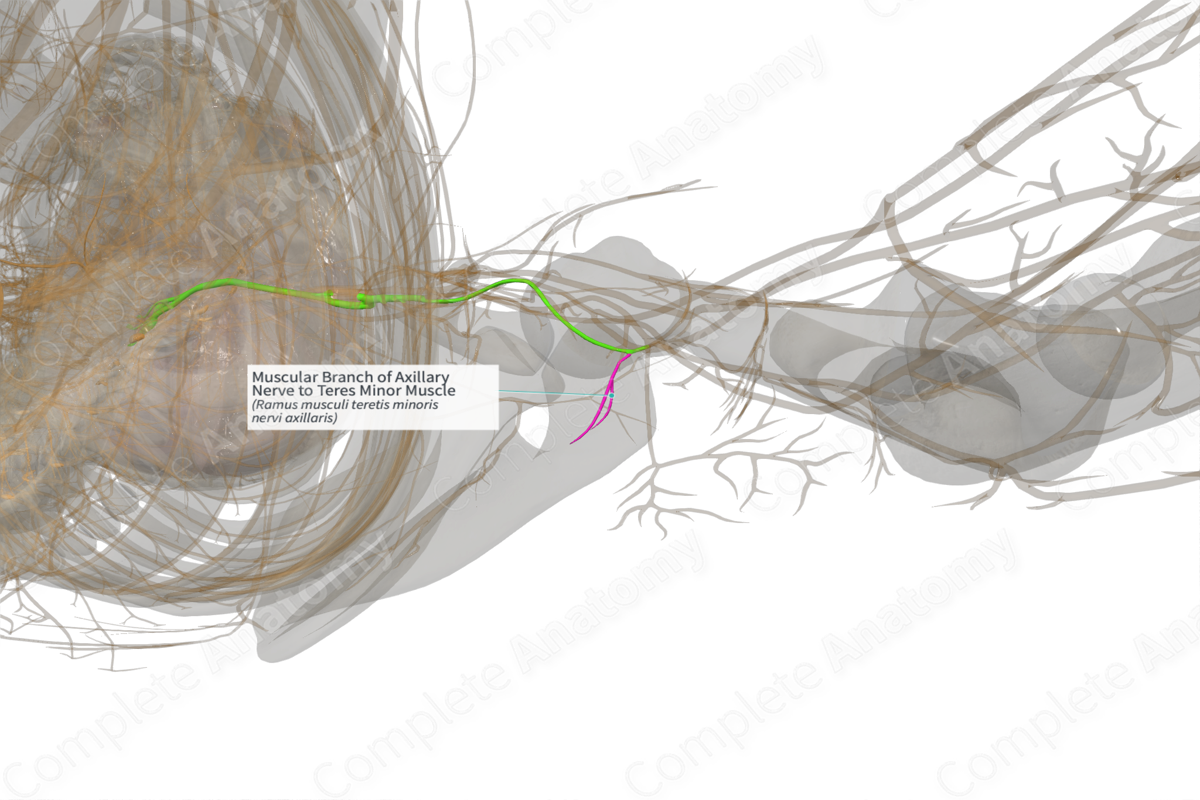
Muscular Branch of Axillary Nerve to Teres Minor Muscle (Left)
Ramus musculi teretis minoris nervi axillaris
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Axillary nerve (C5,C6).
Course: Short course, running posteromedially.
Branches: None.
Supply: Motor innervation to teres minor muscle.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The muscular branch to the teres minor muscle arises from the posterior branch of axillary nerve. It contains motor neurons which come from the C5 and C6 cervical spinal roots.
Course
The axillary nerve, which originates from the posterior cord of brachial plexus, curves back inferior to the glenohumeral articular capsule, and traverses through the quadrangular space bounded above by subscapularis and teres minor muscles. Here the axillary nerve divides into anterior and posterior branches, which provide motor innervation to deltoid and teres minor muscles (Zhao et al., 2001; Loukas et al., 2009).
The posterior branch runs medially and posteriorly along the attachment of the lateral head of triceps, inferior to the glenoid rim for approximately 1 cm. The nerve to teres minor courses medially along the posterior aspect of the inferior part of the glenoid rim, having an intimate association with the glenoid and shoulder joint capsule for approximately 2 cm, before entering the muscle at its inferior border.
The anterior branch of the axillary nerve winds around the neck of the humerus to innervate the deltoid muscle.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The muscular branch of axillary nerve to teres minor provides motor innervation to teres minor muscle.
References
Loukas, M., Grabska, J., Tubbs, R. S., Apaydin, N. and Jordan, R. (2009) 'Mapping the axillary nerve within the deltoid muscle', Surg Radiol Anat, 31(1), pp. 43-7.Zhao, X., Hung, L. K., Zhang, G. M. and Lao, J. (2001) 'Applied anatomy of the axillary nerve for selective neurotization of the deltoid muscle', Clin Orthop Relat Res, (390), pp. 244-51.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





