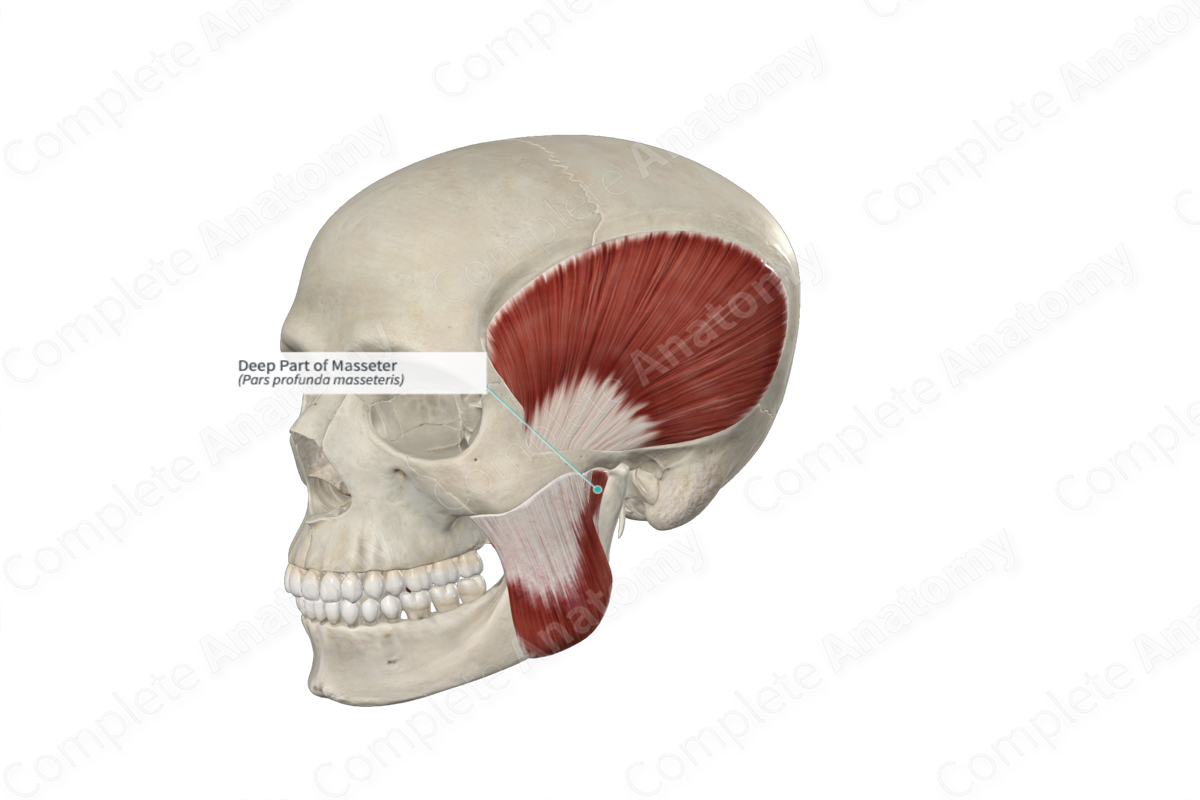
Quick Facts
Origin: Inferior aspect of zygomatic arch.
Insertion: Lateral aspect of coronoid process and ramus of mandible.
Action: Elevates mandible; assists in protraction of mandible.
Innervation: Masseteric nerve (CN V3).
Arterial Supply: Masseteric, transverse facial, and facial arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The deep part of the masseter muscle originates from the inferior aspect of the zygomatic arch and fascia over the temporalis muscle. It extends inferiorly in a vertical direction. It may also attach to the temporomandibular joint, where it is not covered by the superficial part of the masseter muscle (Standring, 2016).
Insertion
The deep component of the masseter inserts into the lateral aspect of the coronoid process and the superior portion of the ramus of the mandible.
Actions
Overall, the masseter muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- elevates the mandible at the temporomandibular joint;
- assists in protraction of the mandible at the temporomandibular joint (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Trismus
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




