Quick Facts
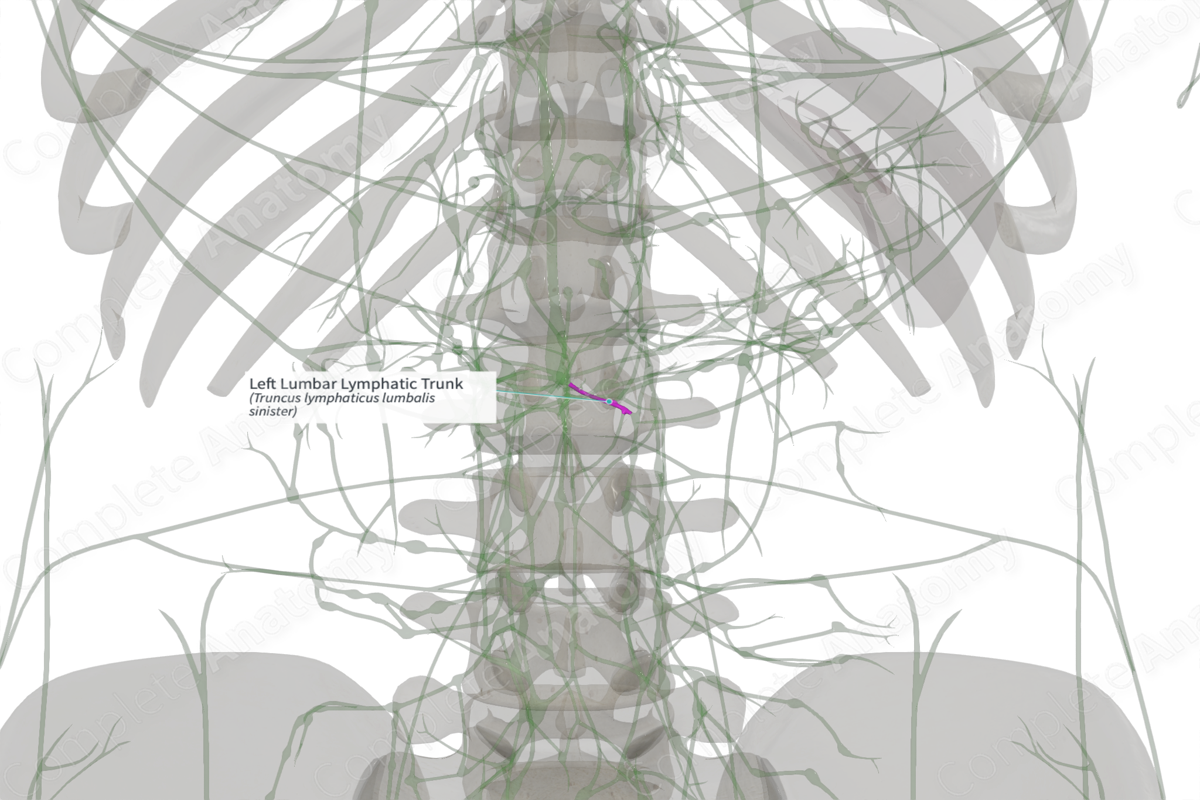
Location: Posterior to abdominal aorta, superior to the left lumbar lymph nodes.
Drainage: Preaortic, lateral aortic, and retroaortic lymph nodes.
Direction of Flow: cisterna chyli > thoracic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description:
Description: (Location & Drainage)
The left lumbar trunk receives lymphatic drainage from the left lumbar lymph nodes (the preaortic, lateral aortic and in most cases the retroaortic lymph nodes) and is usually larger than the right lumbar trunk.
The left lumbar trunk, along with the intestinal trunk, forms the cisterna chyli (45%). The right lumbar trunk most commonly joins the left lumbar trunk (60%) or the intestinal trunk (40%) (Loukas et al., 2007). In other cases (30%), the cisterna chyli is partly formed by the right lumbar trunk, along with accompanying structures including the left lumbar trunk, intestinal trunk, vessels from the retroaortic lymph nodes and intercostal lymph node vessels.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Chylous ascites
References
Loukas, M., Wartmann, C. T., Louis, R. G., Tubbs, R. S., Salter, E. G., Gupta, A. A. and Curry, B. (2007) 'Cisterna chyli: a detailed anatomic investigation', Clin Anat, 20(6), pp. 683-8.
Description:
Description: (Location & Drainage)
The left lumbar trunk receives lymphatic drainage from the left lumbar lymph nodes (the preaortic, lateral aortic and in most cases the retroaortic lymph nodes) and is usually larger than the right lumbar trunk.
The left lumbar trunk, along with the intestinal trunk, forms the cisterna chyli (45%). The right lumbar trunk most commonly joins the left lumbar trunk (60%) or the intestinal trunk (40%) (Loukas et al., 2007). In other cases (30%), the cisterna chyli is partly formed by the right lumbar trunk, along with accompanying structures including the left lumbar trunk, intestinal trunk, vessels from the retroaortic lymph nodes and intercostal lymph node vessels.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products

