Quick Facts
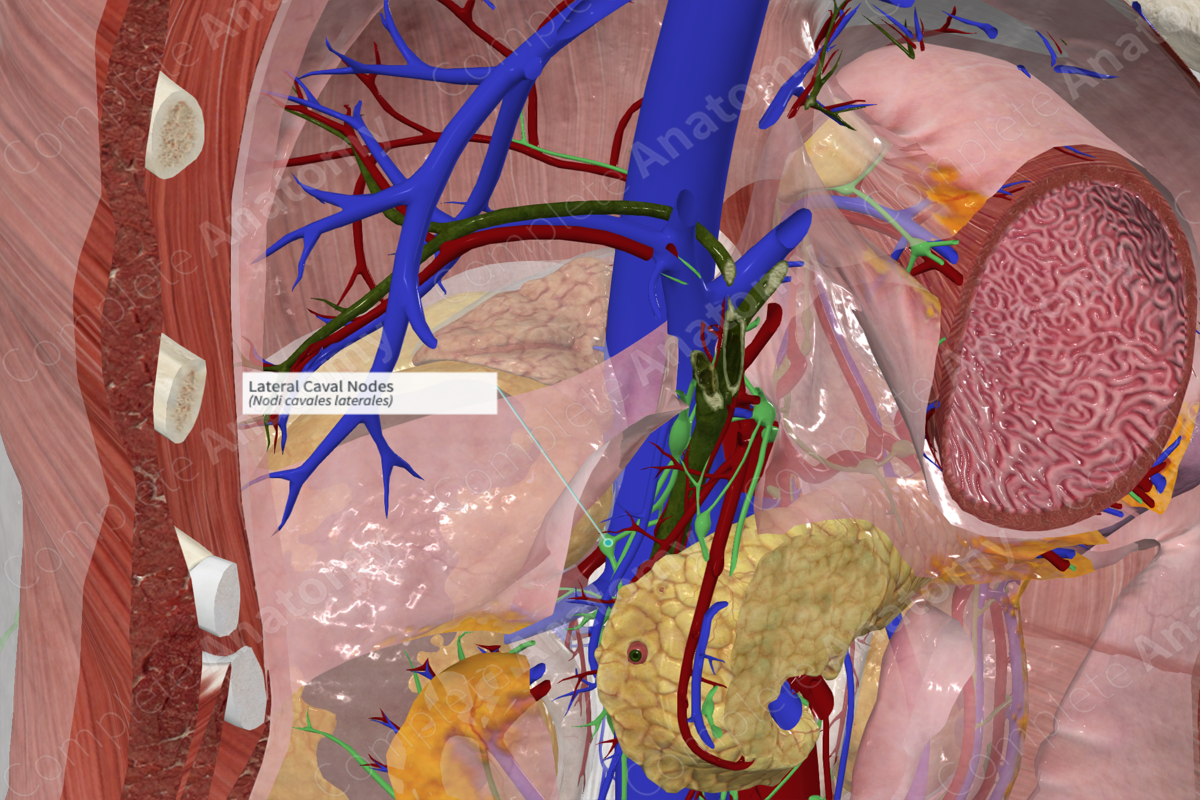
Location: Lateral margin of inferior vena cava.
Drainage: Suprarenal glands, kidneys, ureters, testes/ovaries, uterus, uterine tubes, retroperitoneal viscera (excluding the intestines), and posterior abdominal wall.
Direction of Flow: right lumbar trunk > cisterna chyli > thoracic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description:
Description: (Location & Drainage)
The lateral caval lymph nodes are formed by a group of three to four nodes located on the lateral right side of the inferior vena cava. Nodes are commonly associated around the angle between the inferior vena cava and the right renal vein (Földi et al., 2012).
The lateral caval lymph nodes receive lymph from the suprarenal glands, kidneys, ureters, testes/ovaries, uterus, uterine tubes, retroperitoneal viscera (excluding the intestines) and posterior abdominal wall. Their efferent vessels join the right lumbar trunk, which sends lymph to the cisterna chyli.
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Description:
Description: (Location & Drainage)
The lateral caval lymph nodes are formed by a group of three to four nodes located on the lateral right side of the inferior vena cava. Nodes are commonly associated around the angle between the inferior vena cava and the right renal vein (Földi et al., 2012).
The lateral caval lymph nodes receive lymph from the suprarenal glands, kidneys, ureters, testes/ovaries, uterus, uterine tubes, retroperitoneal viscera (excluding the intestines) and posterior abdominal wall. Their efferent vessels join the right lumbar trunk, which sends lymph to the cisterna chyli.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


