Quick Facts
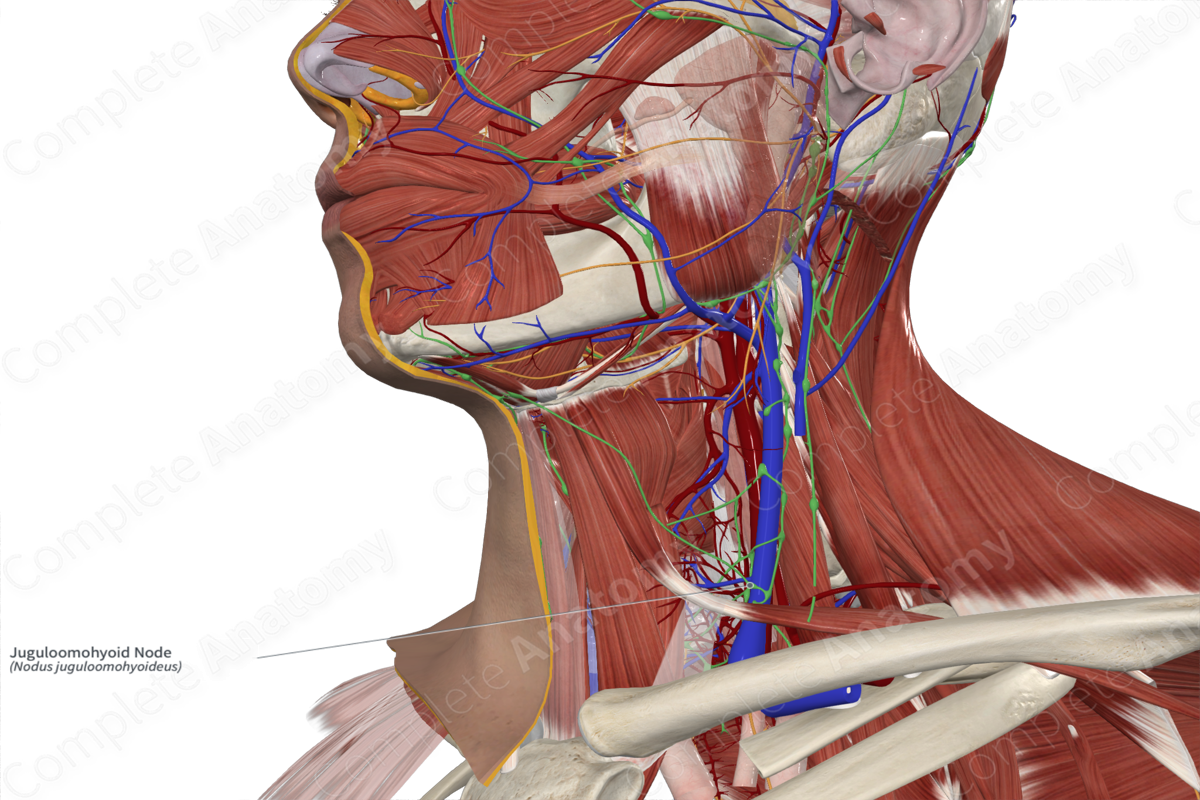
Location: In a triangle in the lateral neck bordered superiorly by the common facial vein, posteriorly by the internal jugular vein, and anteroinferiorly by the superior belly of omohyoid.
Drainage: Tongue.
Direction of Flow: Lateral internal jugular nodes > jugular trunk > thoracic duct (left) or right lymphatic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description
The juguloomohyoid nodes are often closely associated with the intermediate tendon of omohyoid, the juguloomohyoid nodes can be found across a wide area of the lateral neck. These nodes are found in a triangle bound superiorly by the common facial vein, posteriorly by the internal jugular vein, and anteroinferiorly by the superior belly of omohyoid. The number of these nodes can vary from two to ten nodes (Földi et al., 2012).
The juguloomohyoid nodes are principally involved with drainage of lymphatic fluid in the tongue and enlarged juguloomohyoid nodes can be indicative of tongue carcinoma.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Tongue carcinoma
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




