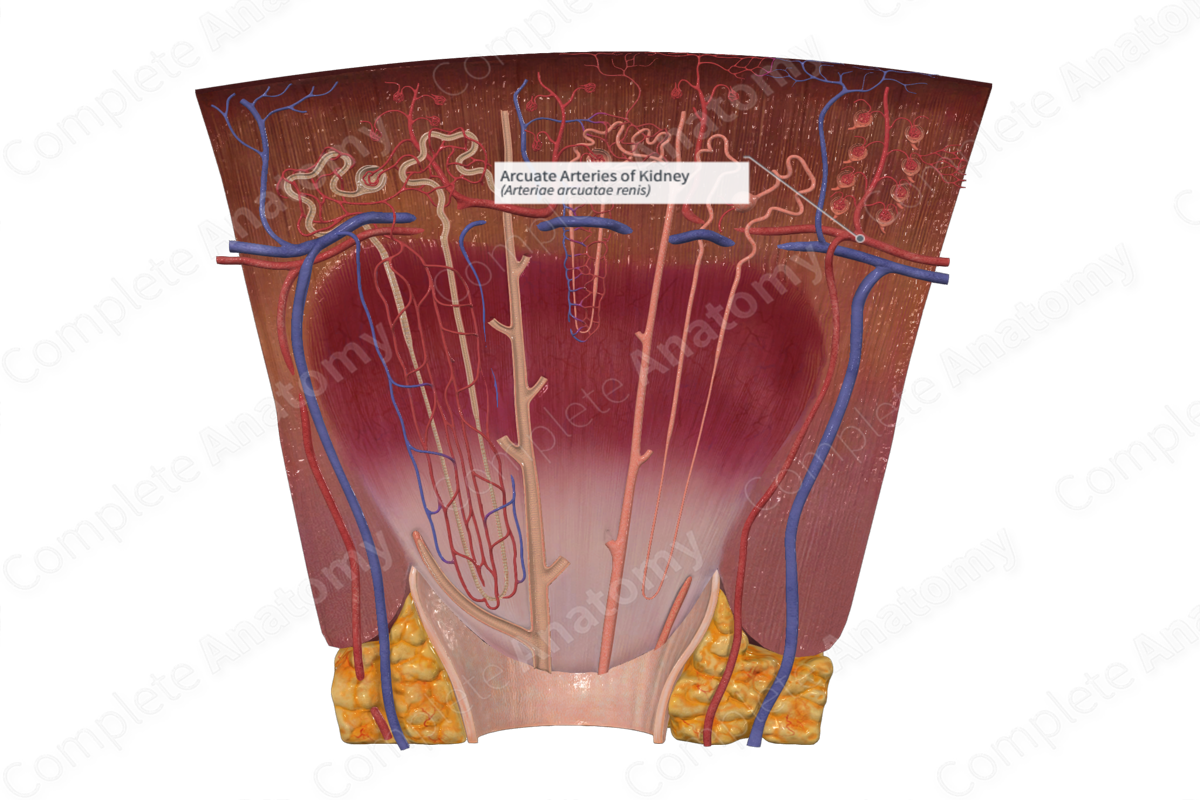
Quick Facts
Origin: interlobar artery;
Branches: interlobular artery and arteriolae rectae;
Distribution: parenchyma of kidney (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Features
At the corticomedullary junction, interlobar arteries divide into arcuate arteries which diverge at right angles. Arcuate arteries are named so due to the fact they arch as they travel between the medulla and the cortex. The branches formed from the arcuate arteries are known as interlobular arteries. The ends of arcuate arteries do not anastomose, instead they terminate in the cortex as additional interlobular arteries (Standring, 2016).
Function
Arcuate arteries facilitate the circulation of blood through the kidneys.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical PracticeElsevier Limited.
